Battle of Thermopylae (480 BC)
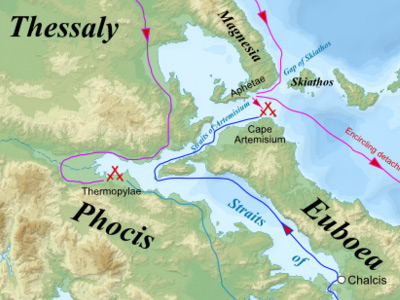
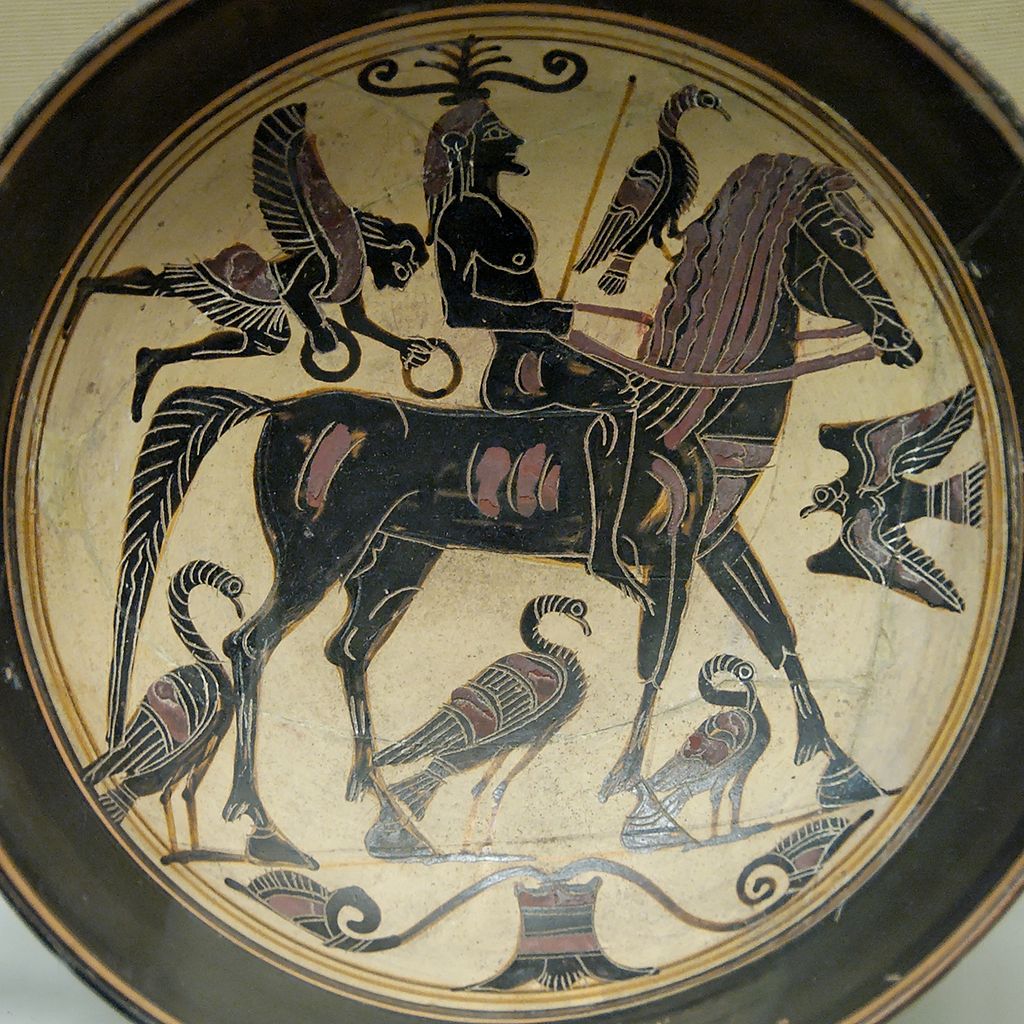
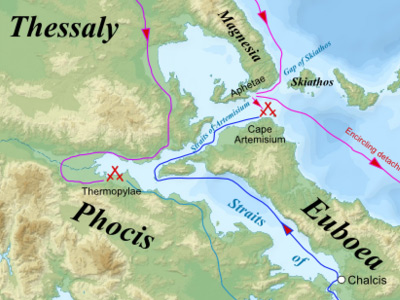
The Battle of Thermopylae (/θərˈmɒpᵻliː/ thər-mop-i-lee; Greek: Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, Machē tōn Thermopylōn) was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, led by King Leonidas of Sparta, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I over the course of three days, during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place simultaneously with the naval battle at Artemisium, in August or September 480 BC, at the narrow coastal pass of Thermopylae ("The Hot Gates"). The Persian invasion was a delayed response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece, which had been ended by the Athenian victory at the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC. Xerxes had amassed a huge army and navy, and set out to conquer all of Greece. The Athenian general Themistocles had proposed that the allied Greeks block the advance of the Persian army at the pass of Thermopylae, and simultaneously block the Persian navy at the Straits of Artemisium.
A Greek force of approximately 7,000 men marched north to block the pass in the middle of 480 BC. The Persian army, alleged by the ancient sources to have numbered over one million, but today considered to have been much smaller (various figures are given by scholars, ranging between about 100,000 and 150,000), arrived at the pass in late August or early September. The vastly outnumbered Greeks held off the Persians for seven days (including three of battle) before the rear-guard was annihilated in one of history's most famous last stands. During two full days of battle, the small force led by Leonidas blocked the only road by which the massive Persian army could pass. After the second day, a local resident named Ephialtes betrayed the Greeks by revealing that a small path led behind the Greek lines. Leonidas, aware that his force was being outflanked, dismissed the bulk of the Greek army and remained to guard their retreat with 300 Spartans, 700 Thespians, 400 Thebans, fighting to death.
At Artemisium, the Greek navy, under the command of the Athenian politician Themistocles, received news of the defeat. Since the Greek strategy required both Thermopylae and Artemisium to be held, and given their losses, it was decided to withdraw to Salamis. The Persians overran Boeotia and then captured the evacuated Athens. The Greek fleet—seeking a decisive victory over the Persian armada—attacked and defeated the invaders at the Battle of Salamis in late 480 BC. Fearful of being trapped in Europe, Xerxes withdrew with much of his army to Asia (losing most to starvation and disease), leaving Mardonius to attempt to complete the conquest of Greece. However, the following year saw a Greek army decisively defeat the Persians at the Battle of Plataea, thereby ending the Persian invasion.
Both ancient and modern writers have used the Battle of Thermopylae as an example of the power of a patriotic army defending its native soil. The performance of the defenders is also used as an example of the advantages of training, equipment, and good use of terrain as force multipliers and has become a symbol of courage against overwhelming odds.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Battle of Thermopylae", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.