French and Indian War (1754–1763)
Events Leading to War
Céloron's Expedition
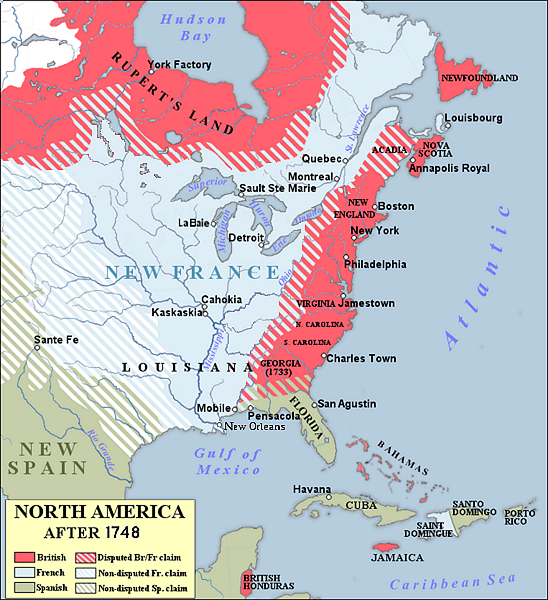
In June 1747, concerned about the incursion and expanding influence of British traders such as George Croghan in the Ohio Country, Roland-Michel Barrin de La Galissonière, the Governor-General of New France, ordered Pierre-Joseph Céloron to lead a military expedition through the area. Its objectives were: to reaffirm to New France's Native allies that their trading arrangements with Europeans were exclusive to those authorized by, or on behalf of New France New France was the territory colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spain in 1763 under the Treaty of Paris. In the 16th century, the lands were used primarily to draw from the wealth of natural resources such as furs through trade with the various indigenous peoples. In the seventeenth century, successful settlements began in Acadia and in Quebec.; to confirm Native assistance in asserting and maintaining (on behalf of French interests), the French claim to original right of discovery, of the whole of the territories which they (the Tribes) inhabited and French explorer's had established first European discovery claim to; to determine the level and extent of British influence (to include any attempt by Britain
New France was the territory colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spain in 1763 under the Treaty of Paris. In the 16th century, the lands were used primarily to draw from the wealth of natural resources such as furs through trade with the various indigenous peoples. In the seventeenth century, successful settlements began in Acadia and in Quebec.; to confirm Native assistance in asserting and maintaining (on behalf of French interests), the French claim to original right of discovery, of the whole of the territories which they (the Tribes) inhabited and French explorer's had established first European discovery claim to; to determine the level and extent of British influence (to include any attempt by Britain The Kingdom of Great Britain was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of England (which included Wales) and Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. or her agents) to seek treaty with them, or other Native tribes to join in alliance against their Tribes, and/or New France; and finally, to impress the Indians of their firmness and resolve, with a French show of force against British Colonial settler incursion; unauthorized trading expeditions, and general trespass against French claims.
The Kingdom of Great Britain was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of England (which included Wales) and Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. or her agents) to seek treaty with them, or other Native tribes to join in alliance against their Tribes, and/or New France; and finally, to impress the Indians of their firmness and resolve, with a French show of force against British Colonial settler incursion; unauthorized trading expeditions, and general trespass against French claims.
Céloron's expedition force consisted of about 200 Troupes de la marine and 30 Indians. The expedition covered about 3,000 miles (4,800 km) between June and November 1749. It went up the St. Lawrence, continued along the northern shore of Lake Ontario, crossed the portage at Niagara, and followed the southern shore of Lake Erie. At the Chautauqua Portage (near present-day Barcelona, New York), the expedition moved inland to the Allegheny River, which it followed to the site of present-day Pittsburgh. There Céloron buried lead plates engraved with the French claim to the Ohio Country. Whenever he encountered British merchants or fur-traders, Céloron informed them of the French claims on the territory and told them to leave.
When Céloron's expedition arrived at Logstown, the Native Americans in the area informed Céloron that they owned the Ohio Country and that they would trade with the British regardless of the French. Céloron continued south until his expedition reached the confluence of the Ohio and the Miami rivers, which lay just south of the village of Pickawillany, the home of the Miami chief known as "Old Briton". Céloron threatened "Old Briton" with severe consequences if he continued to trade with the British. "Old Briton" ignored the warning. Disappointed, Céloron returned to Montreal in November 1749.
In his extensively detailed report, Céloron wrote, "All I can say is that the Natives of these localities are very badly disposed towards the French, and are entirely devoted to the English. I don't know in what way they could be brought back." Even before his return to Montreal, reports on the situation in the Ohio Country were making their way to London and Paris, each side proposing that action be taken. William Shirley, the expansionist governor of the Province of Massachusetts Bay, was particularly forceful, stating that British colonists would not be safe as long as the French were present. Conflicts between the colonies, accomplished through raiding parties that included Indian allies, had taken place for decades, leading to a brisk trade in European colonial captives from either side.
Negotiations
In 1749 the British government gave land to the Ohio Company of Virginia for the purpose of developing trade and settlements in the Ohio Country. The grant required that it settle 100 families in the territory, and construct a fort for their protection. But, as the territory was also claimed by Pennsylvania, both colonies began pushing for action to improve their respective claims. In 1750 Christopher Gist, acting on behalf of both Virginia and the company, explored the Ohio territory and opened negotiations with the Indian tribes at Logstown. He completed the 1752 Treaty of Logstown in which the local Indians, through their "Half-King" Tanacharison and an Iroquois representative, agreed to terms that included permission to build a "strong house" at the mouth of the Monongahela River (the site of present-day Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania). By the late 17th century, the Iroquois had pushed many tribes out of the Ohio Valley, and kept it as hunting ground by right of conquest.
The War of the Austrian Succession (whose North American theater is known as King George's War) formally ended in 1748 with the signing of the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle. The treaty was primarily focused on resolving issues in Europe. The issues of conflicting territorial claims between British and French colonies in North America were turned over to a commission to resolve, but it reached no decision. Frontiers from between Nova Scotia and Acadia in the north, to the Ohio Country in the south, were claimed by both sides. The disputes also extended into the Atlantic Ocean, where both powers wanted access to the rich fisheries of the Grand Banks off Newfoundland.
Attack on Pickawillany
On March 17, 1752, the Governor-General of New France, Marquis de la Jonquière, died and was temporarily replaced by Charles le Moyne de Longueuil. His permanent replacement, the Marquis Duquesne, did not arrive in New France until 1752 to take over the post. The continuing British activity in the Ohio territories prompted Longueuil to dispatch another expedition to the area under the command of Charles Michel de Langlade, an officer in the Troupes de la Marine. Langlade was given 300 men, including French-Canadians and warriors of the Ottawa. His objective was to punish the Miami people of Pickawillany for not following Céloron's orders to cease trading with the British. On June 21, the French war party attacked the trading centre at Pickawillany, capturing three traders and killing 14 people of the Miami nation, including Old Briton. He was reportedly ritually cannibalized by some aboriginal members of the expedition.
French Fort Construction
In the spring of 1753, Paul Marin de la Malgue was given command of a 2,000-man force of Troupes de la Marine and Indians. His orders were to protect the King's land in the Ohio Valley from the British. Marin followed the route that Céloron had mapped out four years earlier, but where Céloron had limited the record of French claims to the burial of lead plates, Marin constructed and garrisoned forts. He first constructed Fort Presque Isle (near present-day Erie, Pennsylvania) on Lake Erie's south shore. He had a road built to the headwaters of LeBoeuf Creek. Marin constructed a second fort at Fort Le Boeuf (present-day Waterford, Pennsylvania), designed to guard the headwaters of LeBoeuf Creek. As he moved south, he drove off or captured British traders, alarming both the British and the Iroquois. Tanaghrisson, a chief of the Mingo, who were remnants of Iroquois and other tribes who had been driven west by colonial expansion. He intensely disliked the French (whom he accused of killing and eating his father). Traveling to Fort Le Boeuf, he threatened the French with military action, which Marin contemptuously dismissed.
The Iroquois sent runners to the manor of William Johnson in upstate New York. The British Superintendent for Indian Affairs in the New York region and beyond, Johnson was known to the Iroquois as Warraghiggey, meaning "He who does great things." He spoke their languages and had become a respected honorary member of the Iroquois Confederacy in the area. In 1746, Johnson was made a colonel of the Iroquois. Later he was commissioned as a colonel of the Western New York Militia. They met at Albany, New York with Governor Clinton and officials from some of the other American colonies. Mohawk Chief Hendrick, Speaker of their tribal council, insisted that the British abide by their obligations and block French expansion. When Clinton did not respond to his satisfaction, Chief Hendrick said that the "Covenant Chain", a long-standing friendly relationship between the Iroquois Confederacy and the British Crown, was broken.
Virginia's Response
Governor Robert Dinwiddie of Virginia was an investor in the Ohio Company, which stood to lose money if the French held their claim. To counter the French military presence in Ohio, in October 1753 Dinwiddie ordered the 21-year-old Major George Washington (whose brother was another Ohio Company investor) of the Virginia Regiment to warn the French to leave Virginia territory. Washington left with a small party, picking up along the way Jacob Van Braam as an interpreter; Christopher Gist, a company surveyor working in the area; and a few Mingo led by Tanaghrisson. On December 12, Washington and his men reached Fort Le Boeuf.
Jacques Legardeur de Saint-Pierre, who succeeded Marin as commander of the French forces after the latter died on October 29, invited Washington to dine with him. Over dinner, Washington presented Saint-Pierre with the letter from Dinwiddie demanding an immediate French withdrawal from the Ohio Country. Saint-Pierre said, "As to the Summons you send me to retire, I do not think myself obliged to obey it." He told Washington that France's The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. claim to the region was superior to that of the British, since René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle had explored the Ohio Country nearly a century earlier.
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. claim to the region was superior to that of the British, since René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle had explored the Ohio Country nearly a century earlier.
Leaving Fort Le Boeuf early on December 16, Washington and his party arrived in Williamsburg on January 16, 1754. In his report, Washington stated, "The French had swept south", detailing the steps they had taken to fortify the area, and their intention to fortify the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers.
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "French and Indian War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.