Spanish Civil War (1936 to 1939)

The Spanish Civil War (Spanish: Guerra Civil Española), widely known in Spain simply as The Civil War (Spanish: Guerra Civil) or The War (Spanish: La Guerra), took place from 1936 to 1939 and was fought between the Republicans, who were loyal to the democratic, left-leaning and relatively urban Second Spanish Republic in an alliance of convenience with the Anarchists, versus the Nationalists, a falangist, Carlist and a largely aristocratic conservative group led by General Francisco Franco.
Although the war is often portrayed as a struggle between democracy and fascism, some historians consider it more accurately described as a struggle between leftist revolution and rightist counterrevolution. Ultimately, the Nationalists won, and Franco then ruled Spain for the next 36 years, from April 1939 until his death in November 1975.
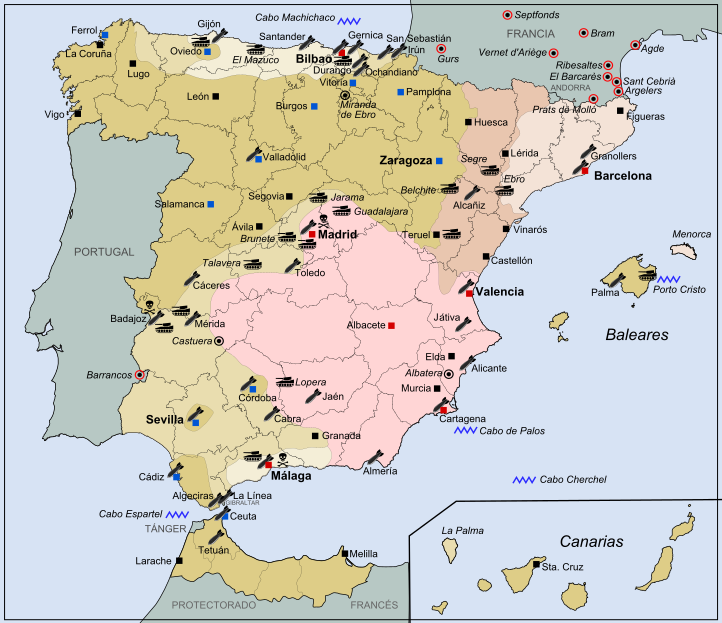
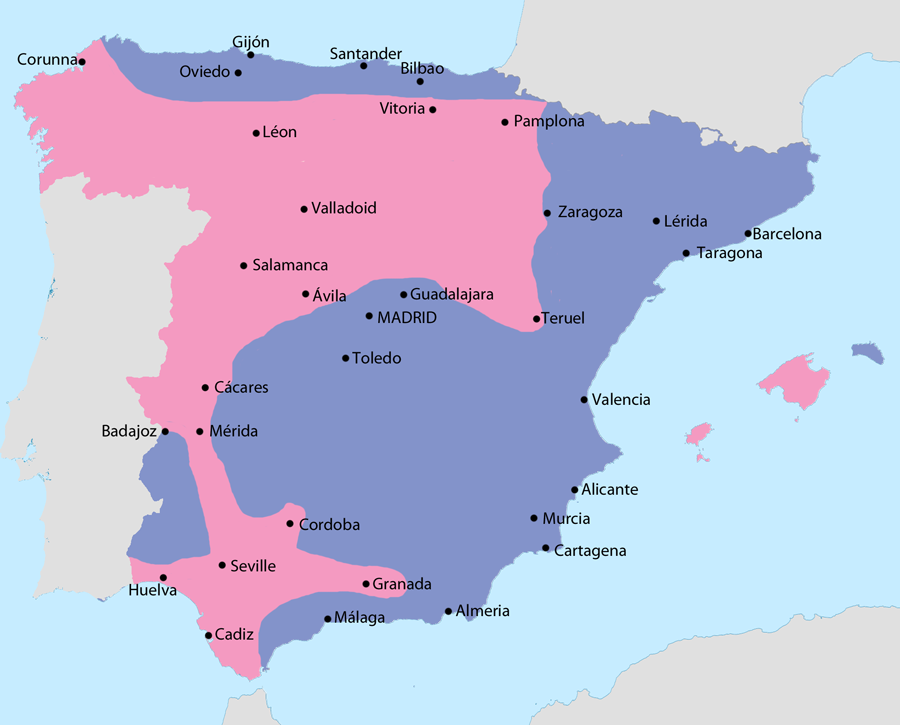
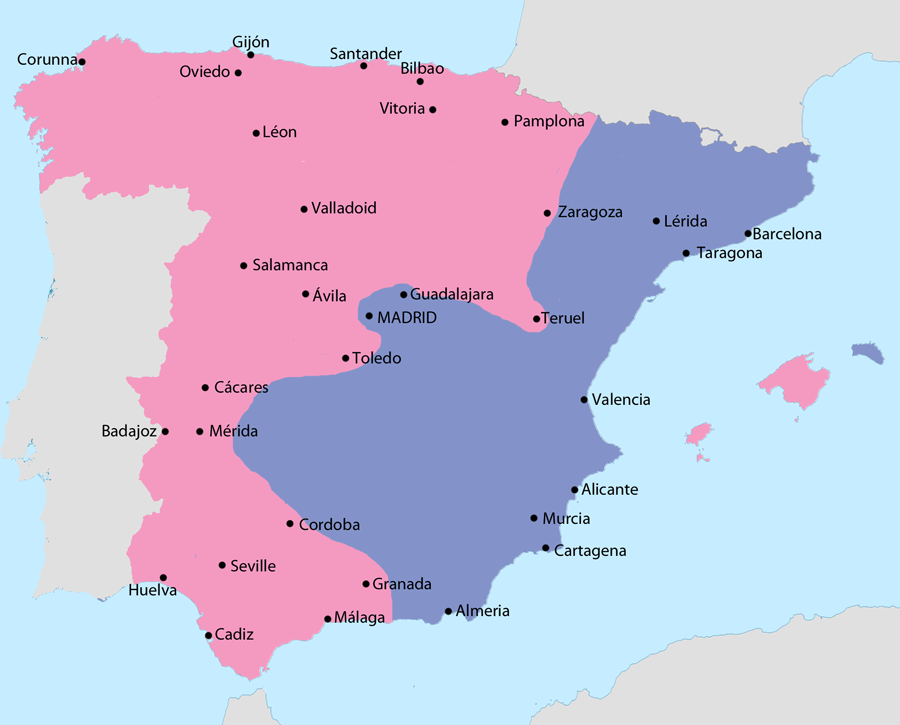
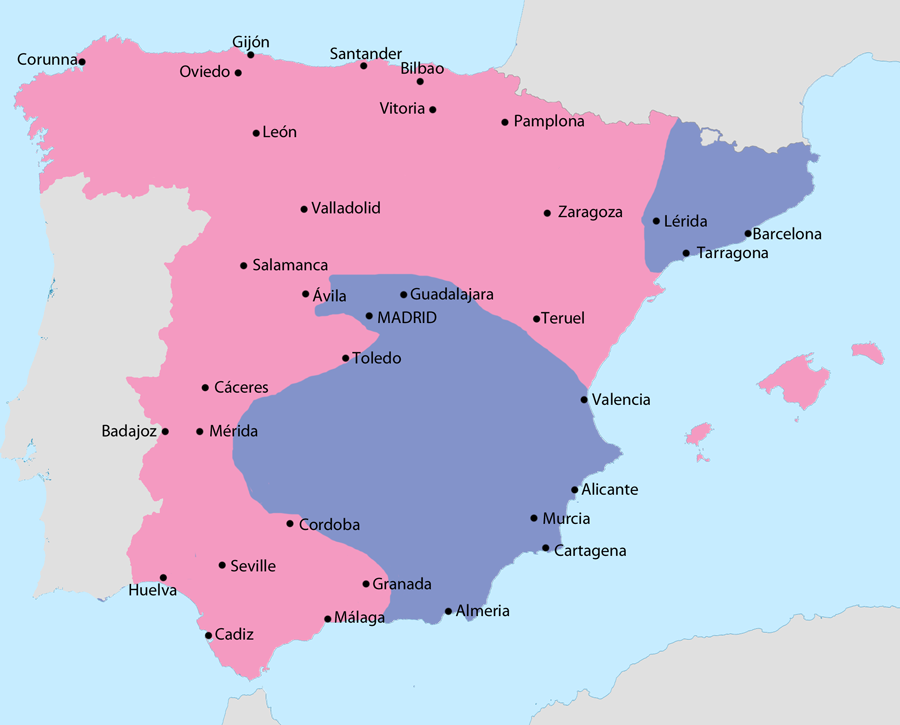
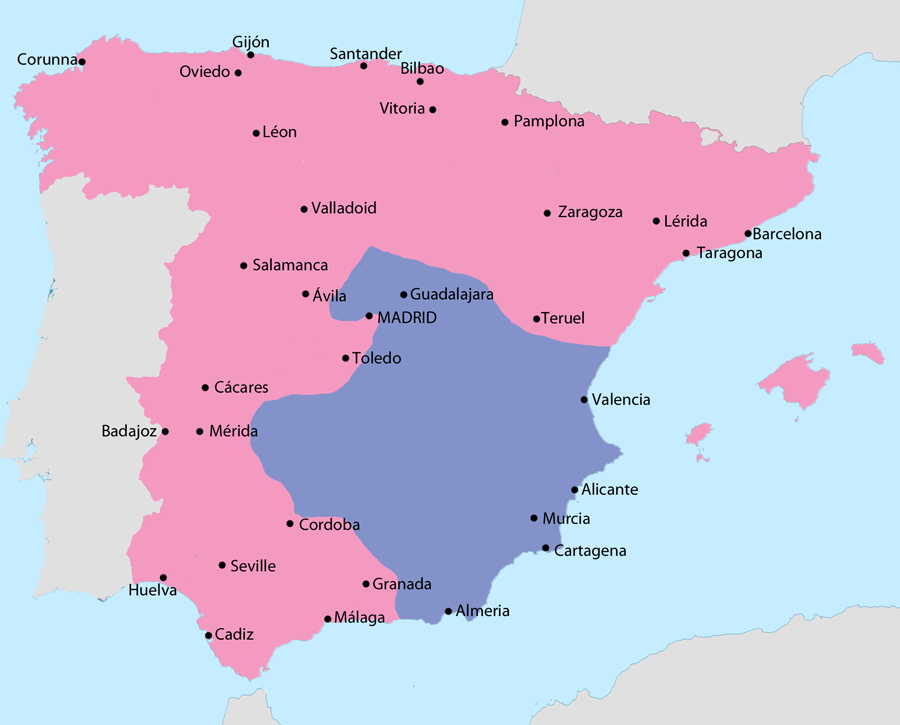
General map of the Spanish Civil War (1936–39)

General map of the Spanish Civil War (1936–39)
( Click image to enlarge)
The war began after a pronunciamiento (declaration of opposition) by a group of generals of the Spanish Republican Armed Forces, originally under the leadership of José Sanjurjo, against the elected, leftist government of the Second Spanish Republic, at the time under the leadership of President Manuel Azaña. The Nationalist group was supported by a number of conservative groups, including the Spanish Confederation of Autonomous Right-wing Groups (Confederación Española de Derechas Autónomas, or CEDA), monarchists such as the religious conservative (Catholic) Carlists, and the Falange Española Tradicionalista y de las Juntas de Ofensiva Nacional Sindicalista, a fascist group. Sanjurjo was killed in an aircraft accident while attempting to return from exile in Portugal, whereupon Franco emerged as the leader of the Nationalists.
The coup was supported by military units in the Spanish protectorate in Morocco, Pamplona, Burgos, Zaragoza, Valladolid, Cádiz, Córdoba and Seville. However, rebelling units in some important cities—such as Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, Bilbao and Málaga—were unable to capture their objectives, and those cities remained under the control of the government. Spain was thus left militarily and politically divided. The Nationalists and the Republican government fought for control of the country. The Nationalist forces received munitions and soldiers from Nazi Germany Nazi Germany (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. and Fascist Italy, while the Republican (Loyalist) side received support from the communist Soviet Union
Nazi Germany (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. and Fascist Italy, while the Republican (Loyalist) side received support from the communist Soviet Union Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. The Soviet Union fall process began with growing unrest in the Union's various constituent national republics developing into an incessant political and legislative conflict between them and the central government. Estonia was the first Soviet republic to declare state sovereignty inside the Union. and socialist Mexico. Other countries, such as the United Kingdom and France, operated an official policy of non-intervention.
Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. The Soviet Union fall process began with growing unrest in the Union's various constituent national republics developing into an incessant political and legislative conflict between them and the central government. Estonia was the first Soviet republic to declare state sovereignty inside the Union. and socialist Mexico. Other countries, such as the United Kingdom and France, operated an official policy of non-intervention.
The Nationalists advanced from their strongholds in the south and west, capturing most of Spain's northern coastline in 1937. They also besieged Madrid and the area to its south and west for much of the war. After large parts of Catalonia were captured in 1938 and 1939, the war ended with the victory of the Nationalists and the exile of thousands of leftist Spaniards, many of whom fled to refugee camps in southern France. Those associated with the losing Republicans were persecuted by the victorious Nationalists. With the establishment of a dictatorship led by General Franco in the aftermath of the war, all right-wing parties fused into the structure of the Franco regime.
The war became notable for the passion and political division it inspired and for the many atrocities. Organized purges occurred in territory captured by Franco's forces to consolidate the future regime. A significant number of killings took place in areas controlled by the Republicans. The extent to which Republican authorities took part in killings in Republican territory varied.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Spanish Civil War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.