Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)

The War of the Government of National Defence
When the news arrived at Paris of the surrender at Sedan of Napoleon III and 80,000 men, the Second Empire was overthrown by a popular uprising in Paris, which forced the proclamation of a Provisional Government and a Third Republic French Third Republic was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940, after the Fall of France during World War II led to the formation of the Vichy government. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the French colonial empire was the second largest colonial empire in the world only behind the British Empire. by general Trochu, Favre and Gambetta at Paris on 4 September, the new government calling itself the Government of National Defence.
French Third Republic was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940, after the Fall of France during World War II led to the formation of the Vichy government. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the French colonial empire was the second largest colonial empire in the world only behind the British Empire. by general Trochu, Favre and Gambetta at Paris on 4 September, the new government calling itself the Government of National Defence.
After the German victory at Sedan, most of the French standing army was either besieged in Metz or prisoner of the Germans, who hoped for an armistice and an end to the war. Bismarck wanted an early peace but had difficulty in finding a legitimate French authority with which to negotiate. The Government of National Defence had no electoral mandate, the Emperor was a captive and the Empress in exile but there had been no abdication de jure and the army was still bound by an oath of allegiance to the defunct imperial régime.
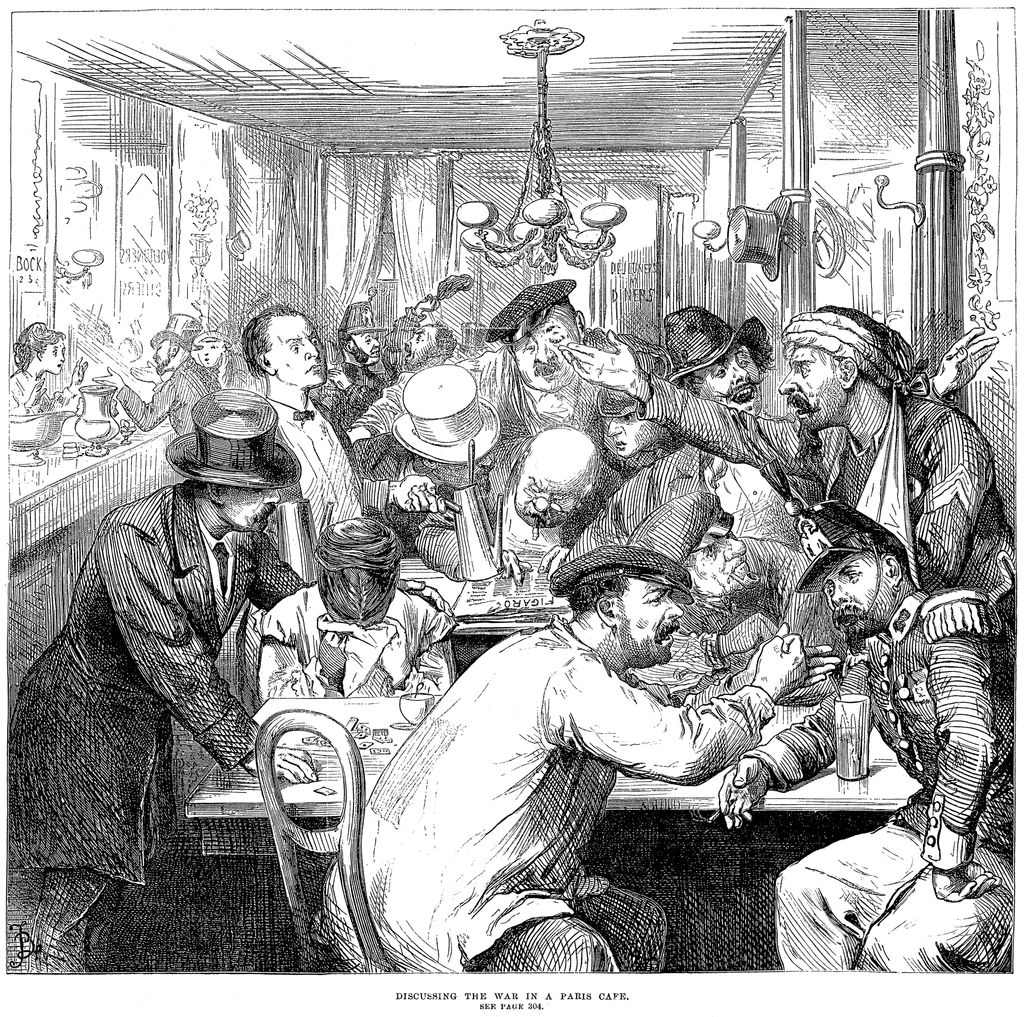

Discussing the War in a Paris Café —a scene published in the Illustrated London News of 17 September 1870
The Germans expected to negotiate an end to the war but immediately ordered an advance on Paris; by 15 September Moltke issued the orders for an investment of Paris and on 20 September the encirclement was complete. Bismarck met Favre on 18 September at the Château de Ferrières and demanded a frontier immune to a French war of revenge, which included Strasbourg, Alsace and most of the Moselle department in Lorraine of which Metz was the capital. In return for an armistice for the French to elect a National Assembly, Bismarck demanded the surrender of Strasbourg and the fortress city of Toul. To allow supplies into Paris, one of the perimeter forts had to be handed over. Favre was unaware that the real aim of Bismarck in making such extortionate demands was to establish a durable peace on the new western frontier of Germany, preferably by a peace with a friendly government, on terms acceptable to French public opinion. An impregnable military frontier was an inferior alternative to him, favoured only by the militant nationalists on the German side.
While the republican government was amenable to war reparations or ceding colonial territories in Africa or in South East Asia to Prussia The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin., Favre on behalf of the Government of National Defense, declared on 6 September that France would not "yield an inch of its territory nor a stone of its fortresses." The republic then renewed the declaration of war, called for recruits in all parts of the country and pledged to drive the German troops out of France by a guerre à outrance. Under these circumstances, the Germans had to continue the war, yet could not pin down any proper military opposition in their vicinity. As the bulk of the remaining French armies were digging-in near Paris, the German leaders decided to put pressure upon the enemy by attacking Paris. By September 15, German troops reached the outskirts of the fortified city. On September 19, the Germans surrounded it and erected a blockade, as already established at Metz.
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin., Favre on behalf of the Government of National Defense, declared on 6 September that France would not "yield an inch of its territory nor a stone of its fortresses." The republic then renewed the declaration of war, called for recruits in all parts of the country and pledged to drive the German troops out of France by a guerre à outrance. Under these circumstances, the Germans had to continue the war, yet could not pin down any proper military opposition in their vicinity. As the bulk of the remaining French armies were digging-in near Paris, the German leaders decided to put pressure upon the enemy by attacking Paris. By September 15, German troops reached the outskirts of the fortified city. On September 19, the Germans surrounded it and erected a blockade, as already established at Metz.
When the war had begun, European public opinion heavily favoured the Germans; many Italians attempted to sign up as volunteers at the Prussian embassy in Florence and a Prussian diplomat visited Giuseppe Garibaldi in Caprera. Bismarck's demand for the return of Alsace caused a dramatic shift in that sentiment in Italy The Kingdom of Italy was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946. The state resulted from a decades-long process, the Risorgimento, of consolidating the different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single state. That process was influenced by the Savoy-led Kingdom of Sardinia, which can be considered Italy's legal predecessor state., which was best exemplified by the reaction of Garibaldi soon after the revolution in Paris, who told the Movimento of Genoa on 7 September 1870 that "Yesterday I said to you: war to the death to Bonaparte. Today I say to you: rescue the French Republic by every means." Garibaldi went to France and assumed command of the Army of the Vosges, with which he operated around Dijon till the end of the war.
The Kingdom of Italy was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946. The state resulted from a decades-long process, the Risorgimento, of consolidating the different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single state. That process was influenced by the Savoy-led Kingdom of Sardinia, which can be considered Italy's legal predecessor state., which was best exemplified by the reaction of Garibaldi soon after the revolution in Paris, who told the Movimento of Genoa on 7 September 1870 that "Yesterday I said to you: war to the death to Bonaparte. Today I say to you: rescue the French Republic by every means." Garibaldi went to France and assumed command of the Army of the Vosges, with which he operated around Dijon till the end of the war.
Siege of Paris
Prussian forces commenced the Siege of Paris on 19 September 1870. Faced with the blockade, the new French government called for the establishment of several large armies in the French provinces. These new bodies of troops were to march towards Paris and attack the Germans there from various directions at the same time. Armed French civilians were to create a guerilla force—the so-called Francs-tireurs—for the purpose of attacking German supply lines.
These developments prompted calls from the German public for a bombardment of the city. Von Blumenthal, who commanded the siege, was opposed to the bombardment on moral grounds. In this he was backed by other senior military figures such as the Crown Prince and Moltke.
Loire Campaign
Dispatched from Paris as the republican government emissary, Léon Gambetta flew over the German lines in a balloon inflated with coal gas from the city's gasworks and organized the recruitment of the Armée de la Loire. Rumors about an alleged German "extermination" plan infuriated the French and strengthened their support of the new regime. Within a few weeks, five new armies totalling more than 500,000 troops were recruited.
The Germans dispatched some of their troops to the French provinces to detect, attack and disperse the new French armies before they could become a menace. The Germans were not prepared for an occupation of the whole of France.
On 10 October, hostilities began between German and French republican forces near Orléans. At first, the Germans were victorious but the French drew reinforcements and defeated the Germans at the Battle of Coulmiers on 9 November. After the surrender of Metz, more than 100,000 well-trained and experienced German troops joined the German 'Southern Army'. The French were forced to abandon Orléans on 4 December, and were finally defeated at the Battle of Le Mans (10–12 January). A second French army which operated north of Paris was turned back at the Battle of Amiens (27 November), the Battle of Bapaume (3 January 1871) and the Battle of St. Quentin (13 January).
Northern Campaign
Following the Army of the Loire's defeats, Gambetta turned to General Faidherbe's Army of the North. The army had achieved several small victories at towns such as Ham, La Hallue, and Amiens and was protected by the belt of fortresses in northern France, allowing Faidherbe's men to launch quick attacks against isolated Prussian units, then retreat behind the fortresses. Despite access to the armaments factories of Lille, the Army of the North suffered from severe supply difficulties, which depressed morale. In January 1871, Gambetta forced Faidherbe to march his army beyond the fortresses and engage the Prussians in open battle. The army was severely weakened by low morale, supply problems, the terrible winter weather and low troop quality, whilst general Faidherbe was unable to command due to his poor health, the result of decades of campaigning in West Africa. At the Battle of St. Quentin, the Army of the North suffered a crushing defeat and was scattered, releasing thousands of Prussian soldiers to be relocated to the East.
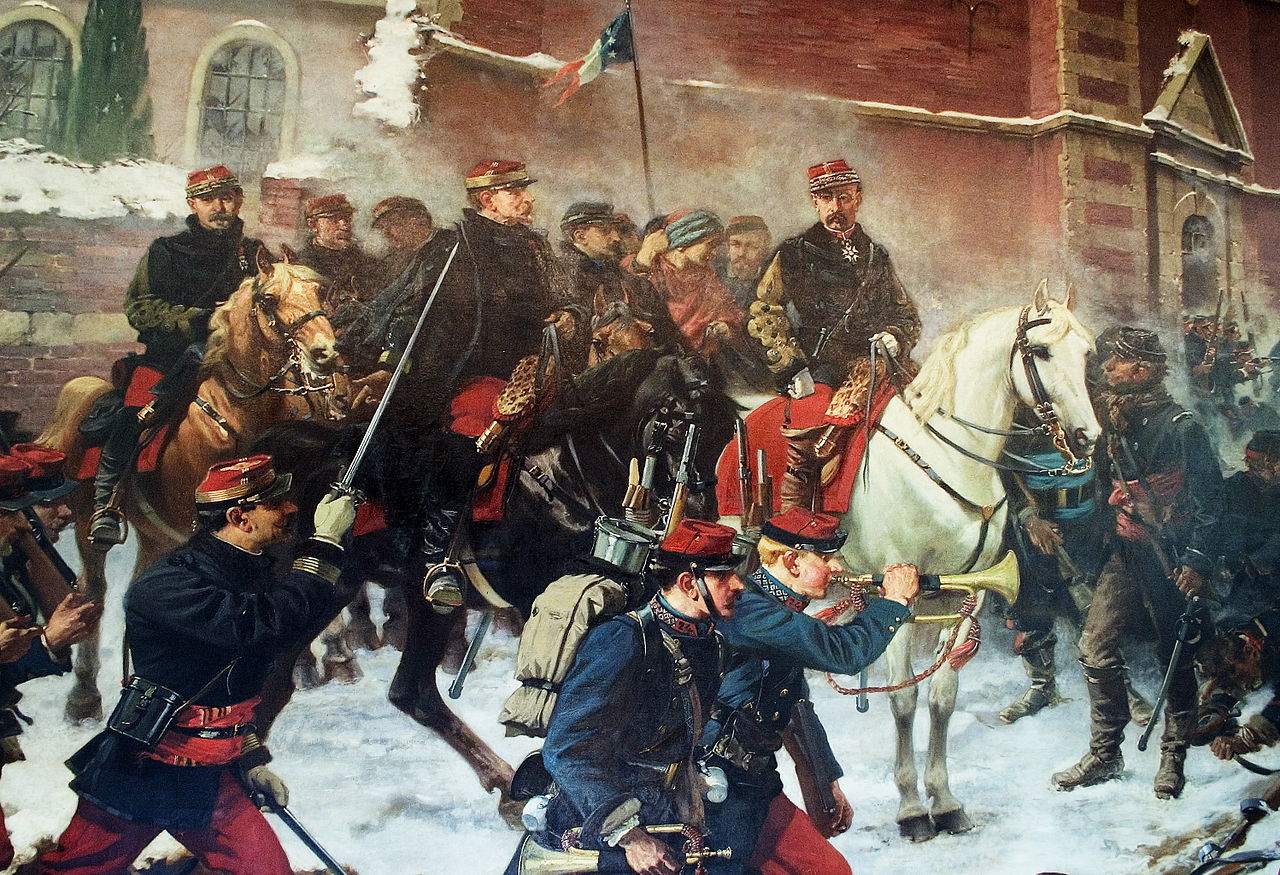

The Battle of Bapaume (1871) took place from 2–3 January 1871, during the Franco-Prussian War in and around Biefvillers-lès-Bapaume and Bapaume. The Prussian advance was stopped by Genéral Louis Léon César Faidherbe at the head of the Armée du Nord.
Eastern Campaign
Following the destruction of the French Army of the Loire, remnants of the Loire army gathered in eastern France to form the Army of the East, commanded by general Charles-Denis Bourbaki. In a final attempt to cut the German supply lines in northeast France, Bourbaki's army marched north to attack the Prussian siege of Belfort and relieve the defenders.
In the battle of the Lisaine, Bourbaki's men failed to break through German lines commanded by General August von Werder. Bringing in the German 'Southern Army', General von Manteuffel then drove Bourbaki's army into the mountains near the Swiss border. Facing annihilation, the last intact French army crossed the border and was disarmed and interned by the neutral Swiss near Pontarlier (1 February).
Armistice
On 26 January 1871 the Government of National Defence based in Paris negotiated an armistice with the Prussians. With Paris starving, and Gambetta's provincial armies reeling from one disaster after another, French foreign minister Favre went to Versailles on 24 January to discuss peace terms with Bismarck. Bismarck agreed to end the siege and allow food convoys to immediately enter Paris (including trains carrying millions of German army rations), on condition that the Government of National Defence surrender several key fortresses outside Paris to the Prussians. Without the forts, the French Army would no longer be able to defend Paris.
Although public opinion in Paris was strongly against any form of surrender or concession to the Prussians, the Government realised that it could not hold the city for much longer, and that Gambetta's provincial armies would probably never break through to relieve Paris. President Trochu resigned on 25 January and was replaced by Favre, who signed the surrender two days later at Versailles, with the armistice coming into effect at midnight. Several sources claim that in his carriage on the way back to Paris, Favre broke into tears, and collapsed into his daughter's arms as the guns around Paris fell silent at midnight. At Bordeaux, Gambetta received word from Paris on 29 January that the Government had surrendered. Furious, he refused to surrender. Jules Simon, a member of the Government arrived from Paris by train on 1 February to negotiate with Gambetta. Another group of three ministers arrived in Bordeaux on 5 February and the following day Gambetta stepped down and surrendered control of the provincial armies to the Government of National Defence, which promptly ordered a cease-fire across France.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.