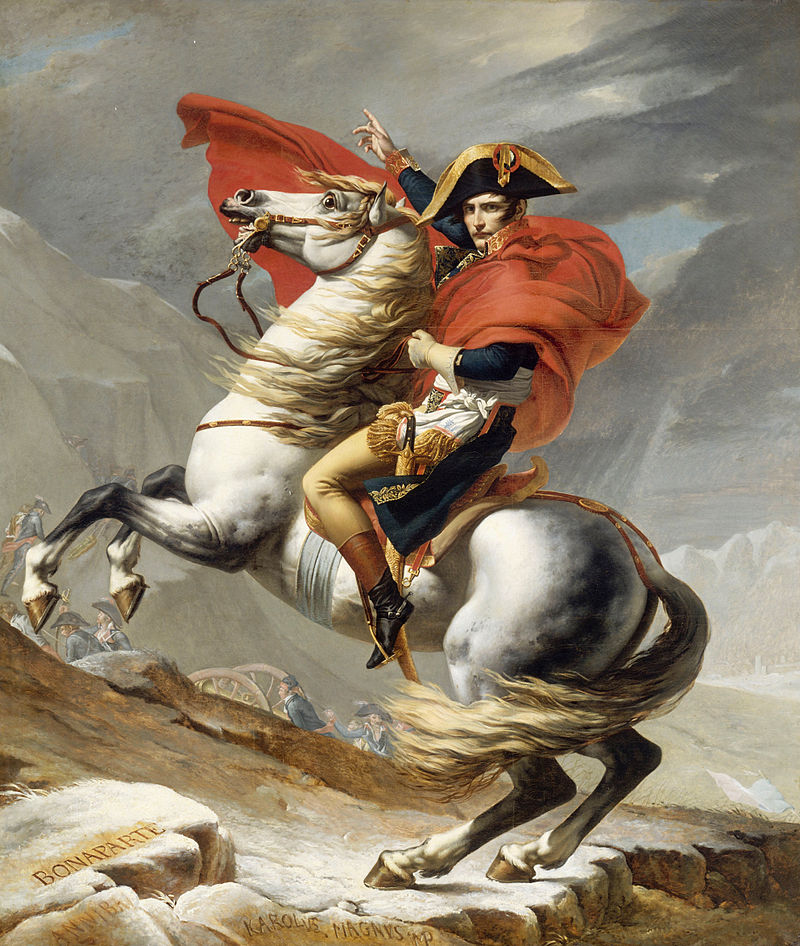
Napoleon Bonaparte (1769-1821)

French Empire
During the Consulate, Napoleon faced several royalist and Jacobin assassination plots, including the Conspiration des poignards (Dagger plot) in October 1800 and the Plot of the Rue Saint-Nicaise (also known as the Infernal Machine) two months later. In January 1804, his police uncovered an assassination plot against him that involved Moreau and which was ostensibly sponsored by the Bourbon family, the former rulers of France.
On the advice of Talleyrand, Napoleon ordered the kidnapping of the Duke of Enghien, violating the sovereignty of Baden. The Duke was quickly executed after a secret military trial, even though he had not been involved in the plot. Enghien's execution infuriated royal courts throughout Europe, becoming one of the contributing political factors for the outbreak of the Napoleonic Wars.
To expand his power, Napoleon Napoleon Bonaparte (1769-1821), was a French military and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led several successful campaigns during the French Revolutionary Wars. As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814, and again in 1815. One of the greatest commanders in history, his wars and campaigns are studied at military schools worldwide. Napoleon Bonaparte » used these assassination plots to justify the creation of an imperial system based on the Roman model. He believed that a Bourbon restoration would be more difficult if his family's succession was entrenched in the constitution. Launching yet another referendum, Napoleon was elected as Emperor of the French by a tally exceeding 99%. As with the Life Consulate two years earlier, this referendum produced heavy participation, bringing out almost 3.6 million voters to the polls.
Napoleon Bonaparte (1769-1821), was a French military and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led several successful campaigns during the French Revolutionary Wars. As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814, and again in 1815. One of the greatest commanders in history, his wars and campaigns are studied at military schools worldwide. Napoleon Bonaparte » used these assassination plots to justify the creation of an imperial system based on the Roman model. He believed that a Bourbon restoration would be more difficult if his family's succession was entrenched in the constitution. Launching yet another referendum, Napoleon was elected as Emperor of the French by a tally exceeding 99%. As with the Life Consulate two years earlier, this referendum produced heavy participation, bringing out almost 3.6 million voters to the polls.
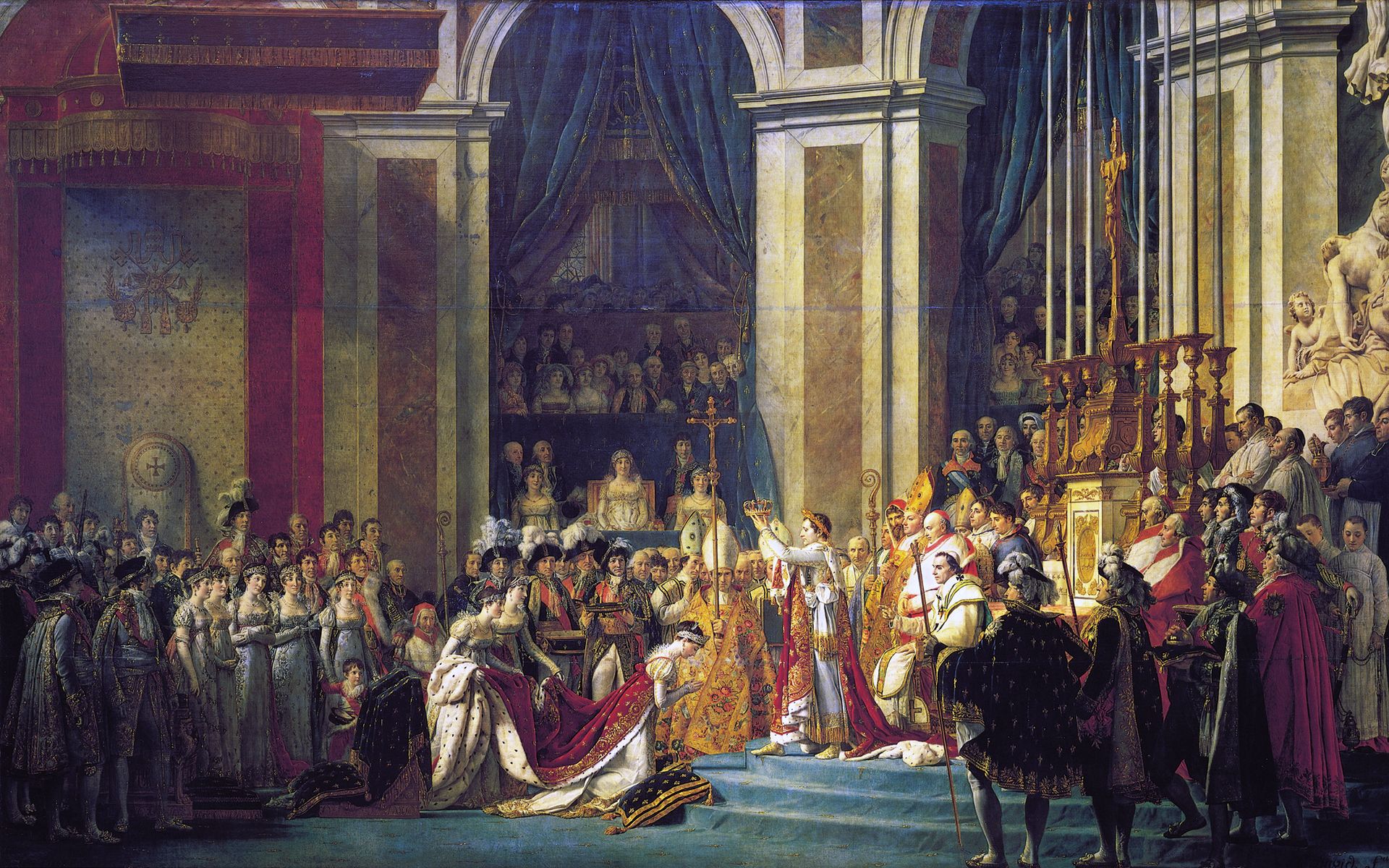
The Coronation of Napoleon by Jacques-Louis David in 1804
Napoleon's coronation took place on 2 December 1804. Two separate crowns were brought for the ceremony: a golden laurel wreath recalling the Roman Empire and a replica of Charlemagne's crown. Napoleon entered the ceremony wearing the laurel wreath and kept it on his head throughout the proceedings. For the official coronation, he raised the Charlemagne crown over his own head in a symbolic gesture, but never placed it on top because he was already wearing the golden wreath. Instead he placed the crown on Josephine's head, the event commemorated in the officially sanctioned painting by Jacques-Louis David. Napoleon was also crowned King of Italy, with the Iron Crown of Lombardy, at the Cathedral of Milan on 26 May 1805. He created eighteen Marshals of the Empire from amongst his top generals to secure the allegiance of the French First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 11 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815. A series of wars, known collectively as the Napoleonic Wars, extended French influence to much of Western Europe and into Poland. army.
First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 11 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815. A series of wars, known collectively as the Napoleonic Wars, extended French influence to much of Western Europe and into Poland. army.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Napoleon", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.













