Pyrrhic War (280–275 BC)
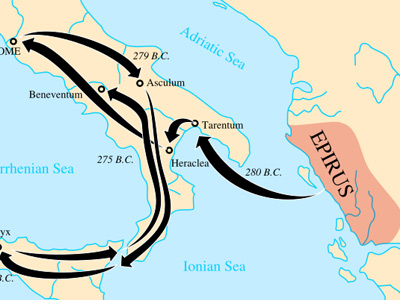
Battle of Asculum (279 BC)
Cassius Dio wrote that during the winter both sides prepared for the next battle. In the spring, Pyrrhus invaded Apulia. Many places were captured or capitulated. The Romans came upon him near Asculum and encamped opposite him. The two sides avoided each other for several days. There were rumours that Publius Decius Mus (one of the two consuls for 279 BC) was getting ready to devote himself like his father and grandfather. In a devotio a Roman commander sacrificed his life by suicidally launching himself into the enemy ranks as a vow to the gods in exchange for a victory when the Roman troops were overwhelmed. This galvanised the Roman soldiers. The rumour alarmed the Italic followers of Pyrrhus, who believed his death would ruin them. Pyrrhus endeavoured to reassure them and ordered to seize alive anyone who wore the garments the Decia family used for devoting themselves. He sent a man to tell Publius Decius that he would not succeed in his intent and after being taken alive he would die miserably. The Roman consuls replied that there was no need to resort to a devotio because the Romans The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. would defeat him without it.
The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. would defeat him without it.
Three ancient historians wrote accounts of this battle: Dionysius of Halicarnassus, Plutarch and Cassius Dio. In the version of Plutarch, the battle took place over two days. In the other two versions it lasted one day. In Cassius Dio's version the Romans won. In Plutarch's version Pyrrhus won. Plutarch noted that Dionysius of Halicarnassus "made no mention two battles, nor of an admitted defeat of the Romans." In fact, Dionysius did not say who won the battle. Plutarch also wrote that Pyrrhus said to someone who was congratulating him: "If we are victorious in one more battle with the Romans, we shall be utterly ruined." This was because he lost a great part of the forces he had brought to Italy and most of his commanders. He could not call up more men from home and his allies in Italy were becoming indifferent. The Romans, instead, could quickly replenish their forces "as if from a fountain gushing forth indoors", and did not lose courage or determination in defeat.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Pyrrhic War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.










