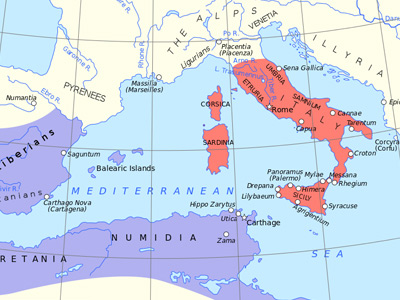
First Punic War (264-241 BC)
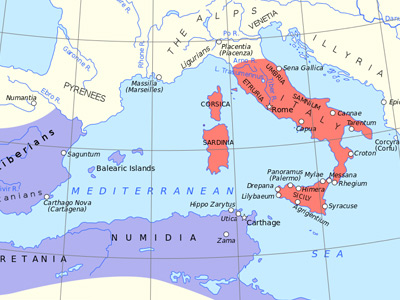
Rome Builds a Fleet
At the beginning of the First Punic War, Rome had virtually no experience in naval warfare, whereas the strong and powerful Carthage had a great deal of experience on the seas thanks to its centuries of sea-based trade. Nevertheless, the growing Roman Republic The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. soon understood the importance of Mediterranean control in the outcome of the conflict.
The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. soon understood the importance of Mediterranean control in the outcome of the conflict.
Origin of Roman Design
The first major Roman fleet was constructed after the victory of Agrigentum in 261 BC. Some historians have speculated that, since Rome lacked advanced naval technology, the design of the warships was probably copied from captured Carthaginian triremes and quinqueremes or from ships that had beached on Roman shores due to storms. According to Polybius, the Romans seized a shipwrecked Carthaginian quinquereme, and used it as a blueprint for their own ships. Other historians have pointed out that Rome did have experience with naval technology, as she patrolled her coasts against piracy. Another possibility is that Rome received technical assistance from its seafaring Sicilian ally, Syracuse. Regardless of the state of their naval technology at the start of the war, Rome quickly adapted.
The Corvus
In order to compensate for the lack of experience, and to make use of standard land military tactics at sea, the Romans equipped their new ships with a special boarding device, the corvus. The Roman military was a land-based army, while Carthage was primarily a naval power. This boarding-bridge allowed the Roman navy to circumvent some of Carthage's naval skills by using their marines to board Carthaginian ships and fight in hand-to-hand combat. Instead of maneuvering to ram, which was the standard naval tactic at the time, corvus equipped ships would maneuver alongside the enemy vessel, deploy the bridge which would attach to the enemy ship through spikes on the end of the bridge, and send legionaries across as boarding parties.
The new weapon would prove its worth in the Battle of Mylae, the first Roman naval victory, and would continue to do so in the following years, especially in the huge Battle of Cape Ecnomus. The addition of the corvus forced Carthage to review its military tactics, and since the city had difficulty in doing so, Rome had the naval advantage.
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "First Punic War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.