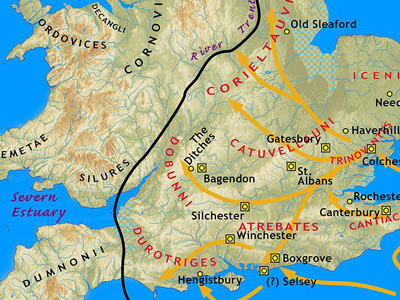
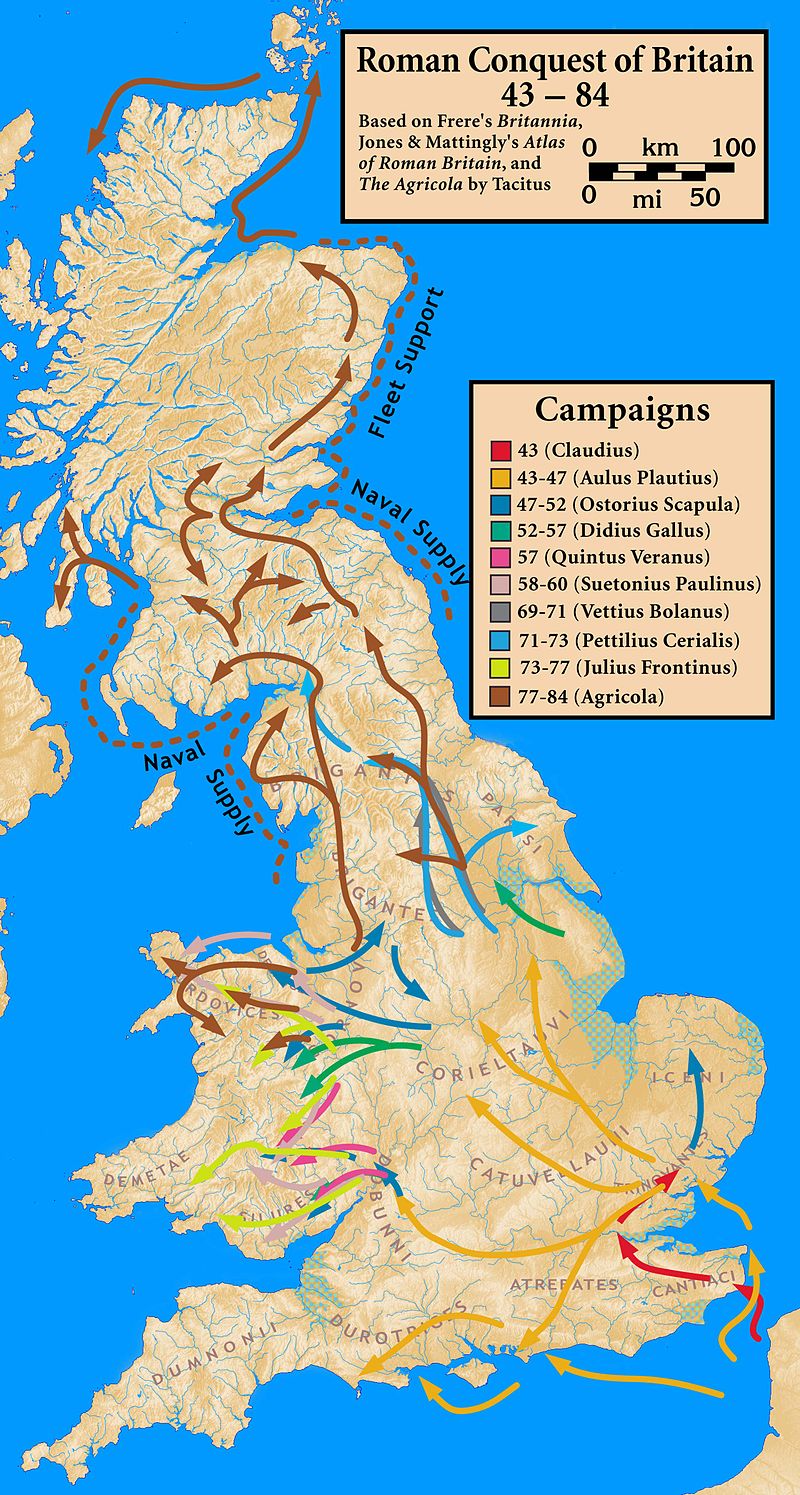
Roman conquest of Britain (43-96 AD)
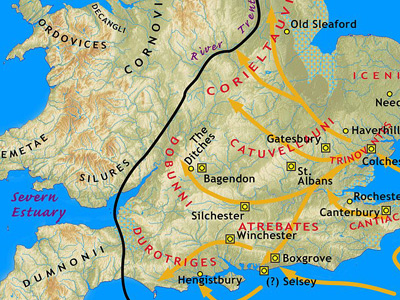
Failure to Conquer Caledonia
Roman occupation was withdrawn to a line subsequently established as one of the limites of the Roman Empire The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. by the construction of Hadrian's Wall. An attempt was made to push this line north to the River Clyde-River Forth area in 142 when the Antonine Wall was constructed. This was once again abandoned after two decades and only subsequently re-occupied on an occasional basis.
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. by the construction of Hadrian's Wall. An attempt was made to push this line north to the River Clyde-River Forth area in 142 when the Antonine Wall was constructed. This was once again abandoned after two decades and only subsequently re-occupied on an occasional basis.
The Romans retreated to the earlier and stronger Hadrian's Wall in the River Tyne-Solway Firth frontier area, this having been constructed around 122. Roman troops, however, penetrated far into the north of modern Scotland several more times. Indeed, there is a greater density of Roman marching camps in Scotland than anywhere else in Europe as a result of at least four major attempts to subdue the area.
The most notable was in 209 when the emperor Septimius Severus, claiming to be provoked by the belligerence of the Maeatae tribe, campaigned against the Caledonian Confederacy, a coalition of Brittonic Pictish tribes of the north of Britain. He used the three legions of the British garrison (augmented by the recently formed 2nd Parthica legion), 9000 imperial guards with cavalry support, and numerous auxiliaries supplied from the sea by the British fleet, the Rhine fleet and two fleets transferred from the Danube for the purpose. According to Dio Cassius, he inflicted genocidal depredations on the natives and incurred the loss of 50,000 of his own men to the attrition of guerrilla tactics before having to withdraw to Hadrian's Wall. He repaired and reinforced the wall with a degree of thoroughness that led most subsequent Roman authors to attribute the construction of the wall to him. It was during the negotiations to purchase the truce necessary to secure the Roman retreat to the wall that the first recorded utterance, attributable with any reasonable degree of confidence, to a native of Scotland was made (as recorded by Dio Cassius). When Septimius Severus's wife, Julia Domna, criticised the sexual morals of the Caledonian women, the wife of a Caledonian chief, Argentocoxos, replied: "We consort openly with the best of men while you allow yourselves to be debauched in private by the worst". The emperor Septimius Severus died at York while planning to renew hostilities, and these plans were abandoned by his son Caracalla.
Later excursions into Scotland by the Romans were generally limited to the scouting expeditions of exploratores in the buffer zone that developed between the walls, trading contacts, bribes to purchase truces from the natives, and eventually the spread of Christianity. The degree to which the Romans interacted with the Gaelic speaking island of Hibernia (modern Ireland) is still unresolved amongst archaeologists in Ireland. The successes and failures of the Romans in subduing the peoples of Britain are still represented in the political geography of the British Isles today.
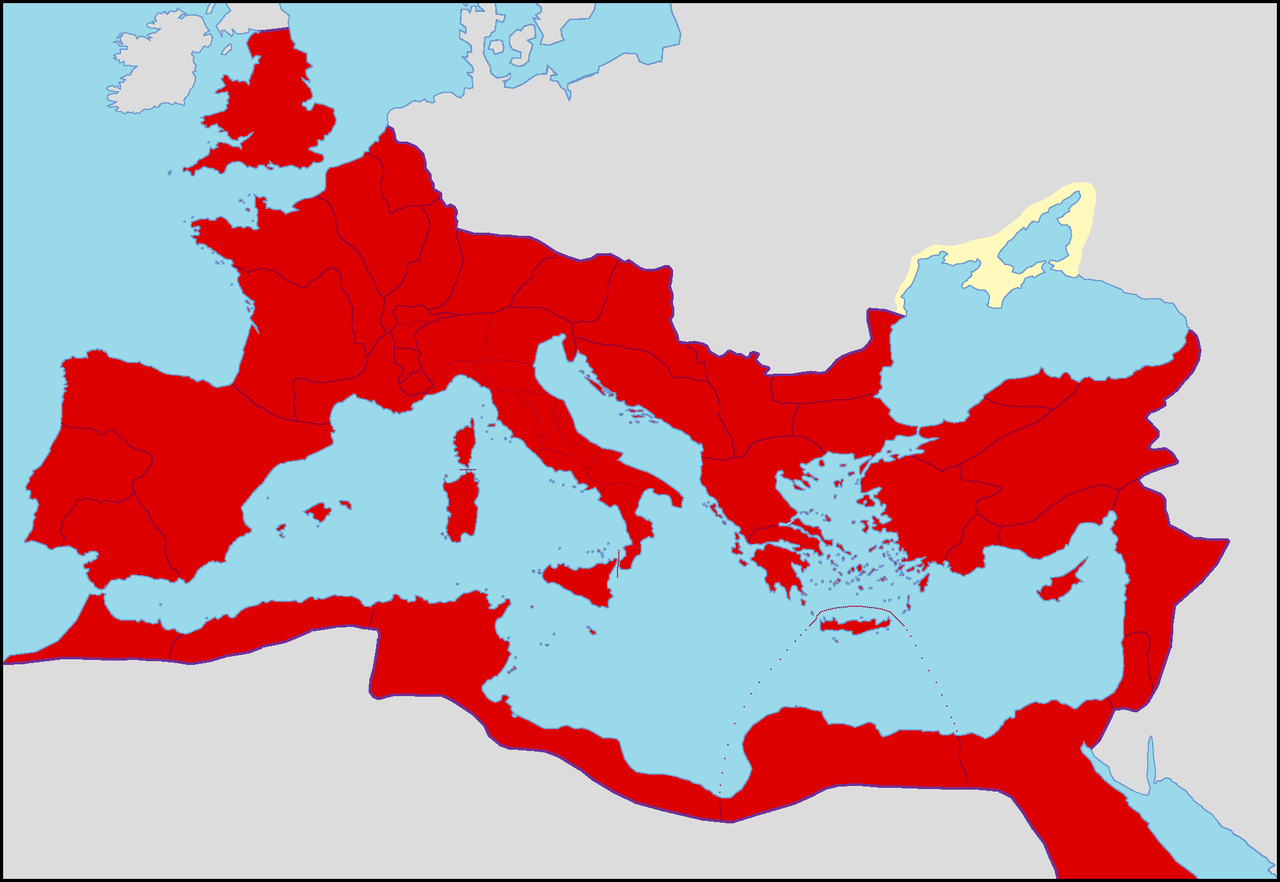
Map of the Roman Empire in 96 AD

Map of the Roman Empire in 96 AD
( Click image to enlarge)
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Roman conquest of Britain", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.