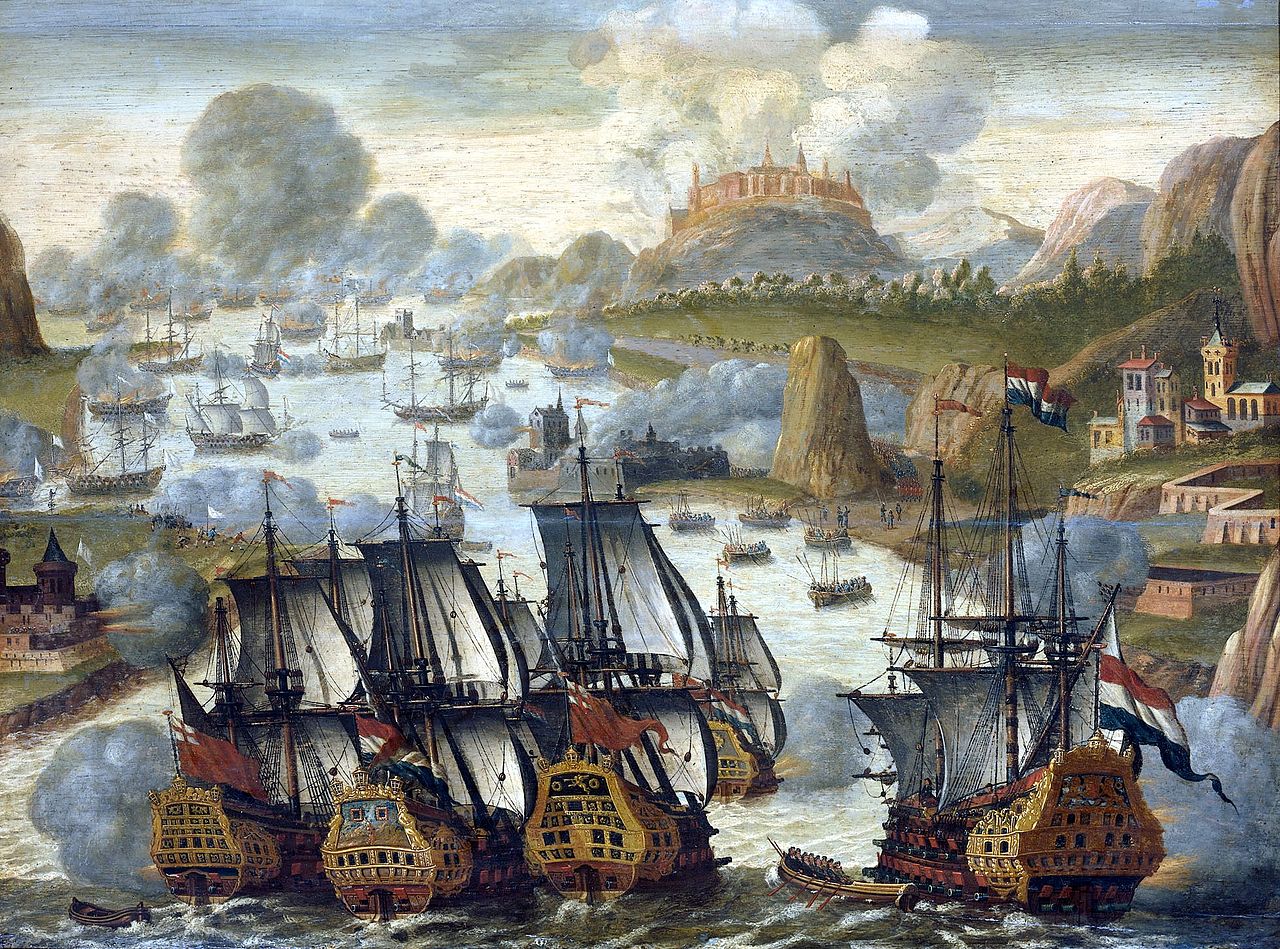
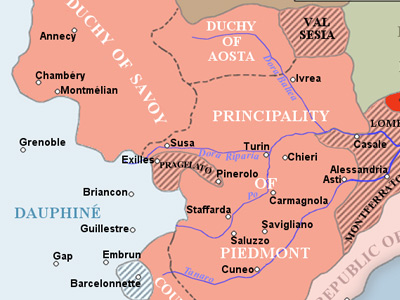
War of the Spanish Succession (1702–1715)

Background of the Spanish Succession
In the late 1690s the declining health of King Charles II of Spain brought to a head the problem of his succession, a problem which had underlain much of European diplomacy for several decades. By the late 17th century Spain was no longer a hegemonic power in Europe, but the Spanish Empire The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. – essentially a vast confederation that covered the globe, which Spaniards usually referred to as a "Monarchy" – remained resilient. Besides Spain, Charles II's other European realms comprised the Balearic Islands, the Spanish Netherlands, Milan, Sicily, Naples, Sardinia, Finale and the State of Presidi on the Tuscan coast; overseas realms included the Philippines, the Spanish West Indies, Florida, and much of North and South America and several North African cities. The empire was in decline, but remained the largest of the European overseas empires, and was still active and influential on the European and global stage.
The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. – essentially a vast confederation that covered the globe, which Spaniards usually referred to as a "Monarchy" – remained resilient. Besides Spain, Charles II's other European realms comprised the Balearic Islands, the Spanish Netherlands, Milan, Sicily, Naples, Sardinia, Finale and the State of Presidi on the Tuscan coast; overseas realms included the Philippines, the Spanish West Indies, Florida, and much of North and South America and several North African cities. The empire was in decline, but remained the largest of the European overseas empires, and was still active and influential on the European and global stage.
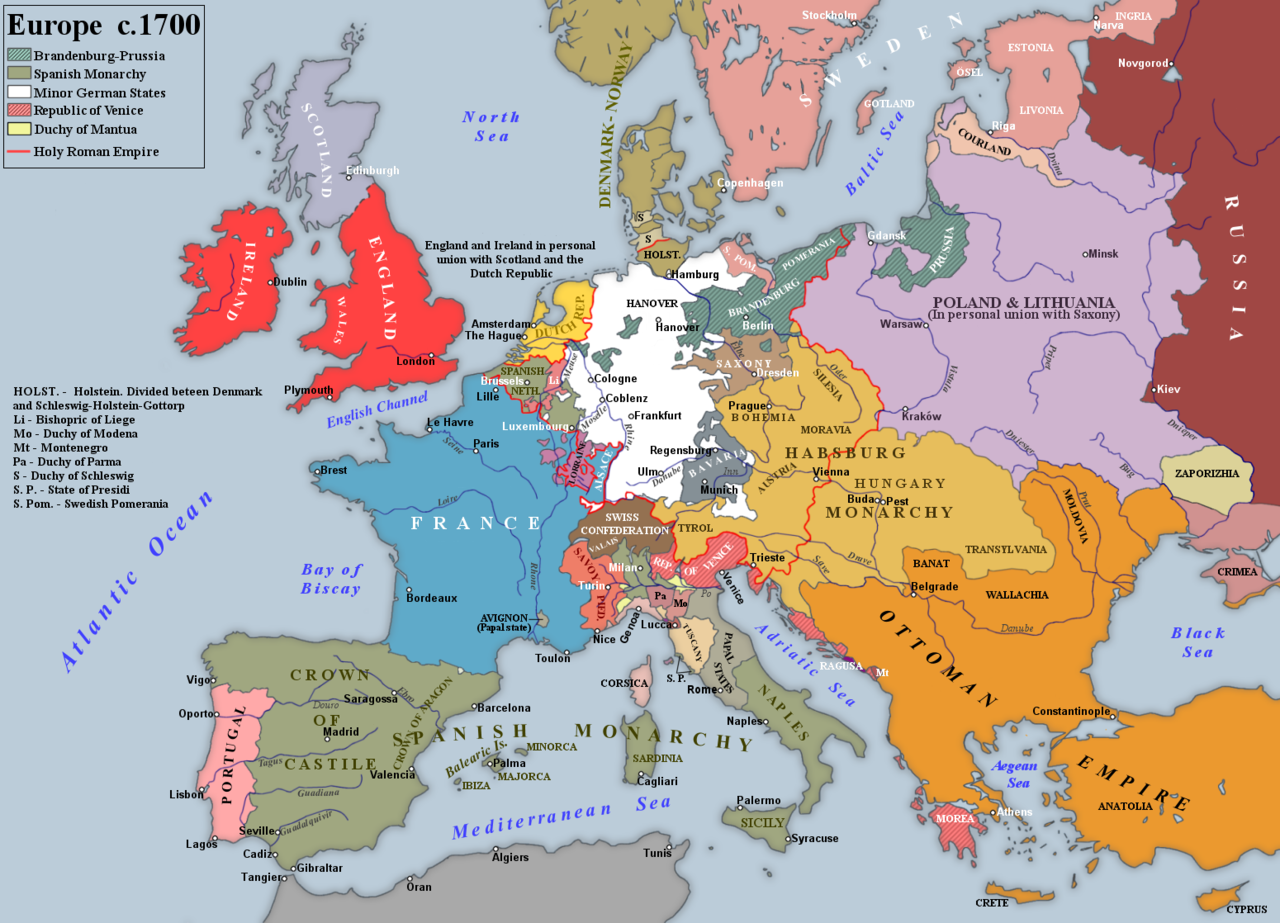
Europe at the beginning of the War of the Spanish Succession

Europe at the beginning of the War of the Spanish Succession
( Click image to enlarge)
Charles II had become king following the death of his father, Philip IV, in 1665, but he was physically weak and incapable of having children; he was the last male Spanish Habsburg and he had survived longer than anyone had expected. When the Treaty of Ryswick (Rijswijk) brought an end to the Nine Years' War (1688–97), European statesmen turned their attention to solve the problem of the Spanish Succession before the death of Charles II should actually take place. Ultimately, the main rivals for the Spanish inheritance were the heirs and descendants of the Bourbon King Louis XIV of France The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic., and the Austrian Habsburg Holy Roman
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic., and the Austrian Habsburg Holy Roman The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. Emperor, Leopold I, both of whom were sons-in-law to Philip IV of Spain and grandsons of Philip III, and both firmly believed in their claims. However, the inheritance was so vast that its transference would dramatically increase either French or Austrian
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. Emperor, Leopold I, both of whom were sons-in-law to Philip IV of Spain and grandsons of Philip III, and both firmly believed in their claims. However, the inheritance was so vast that its transference would dramatically increase either French or Austrian The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire. power which, due to the implied threat of European hegemony, was of the utmost importance to Europe as a whole.
The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire. power which, due to the implied threat of European hegemony, was of the utmost importance to Europe as a whole.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "War of the Spanish Succession", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.