Vietnam War (1955–1975)
Diệm era, 1955–63
Rule
A devout Roman Catholic, Diệm was fervently anti-communist, nationalist, and socially conservative. Historian Luu Doan Huynh notes that "Diệm represented narrow and extremist nationalism coupled with autocracy and nepotism." The majority of Vietnamese people were Buddhist, and were alarmed by actions such as Diệm's dedication of the country to the Virgin Mary.
Beginning in the summer of 1955, Diệm launched the "Denounce the Communists" campaign, during which communists and other anti-government elements were arrested, imprisoned, tortured, or executed. He instituted the death penalty against any activity deemed communist in August 1956. According to Gabriel Kolko about 12,000 suspected opponents of Diệm were killed between 1955 and 1957 and by the end of 1958 an estimated 40,000 political prisoners had been jailed.
In May 1957, Diệm undertook a ten-day state visit to the United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country in North America. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City.. President Eisenhower pledged his continued support, and a parade was held in Diệm's honor in New York City. Although Diệm was publicly praised, in private Secretary of State John Foster Dulles conceded that Diệm had been selected because there were no better alternatives.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country in North America. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City.. President Eisenhower pledged his continued support, and a parade was held in Diệm's honor in New York City. Although Diệm was publicly praised, in private Secretary of State John Foster Dulles conceded that Diệm had been selected because there were no better alternatives.
Former Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara wrote in Argument Without End (1999) that the new American patrons of the Republic of Vietnam (ROV) were almost completely ignorant of Vietnamese culture. They knew little of the language or long history of the country. There was a tendency to assign American motives to Vietnamese actions, though Diệm warned that it was an illusion to believe that blindly copying Western methods would solve Vietnamese problems.
Insurgency in the South, 1954–60
Between 1954 and 1957 there was large-scale but disorganized dissidence in the countryside which the Diệm government succeeded in quelling. In early 1957 South Vietnam enjoyed its first peace in over a decade. Incidents of political violence began to occur in mid-1957, but the government "did not construe it as a campaign, considering the disorders too diffuse to warrant committing major GVN [Government of Vietnam] resources." By early 1959, however, Diệm had come to regard the (increasingly frequent) disorders as an organized campaign and implemented Law 10/59, which made political violence punishable by death and property confiscation. There had been some division among former Viet Minh whose main goal was to hold the elections promised in the Geneva Accords, leading to "wildcat" activities separate from the other communists and anti-GVN activists.
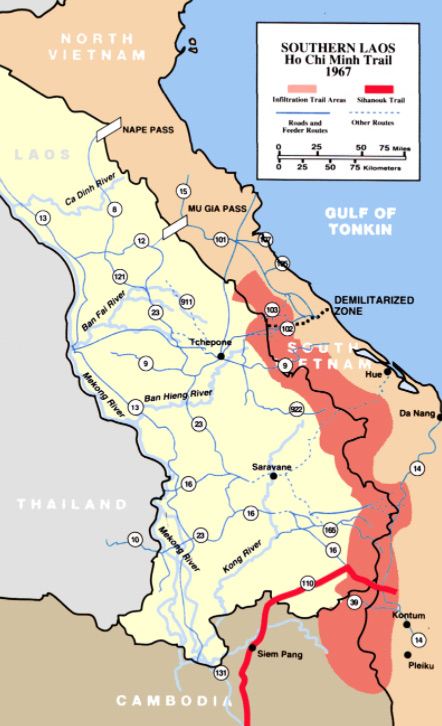
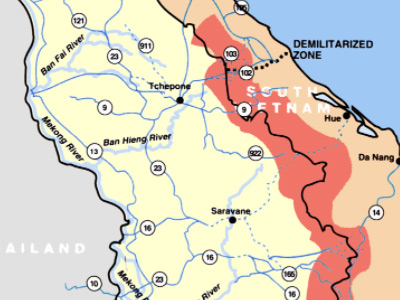
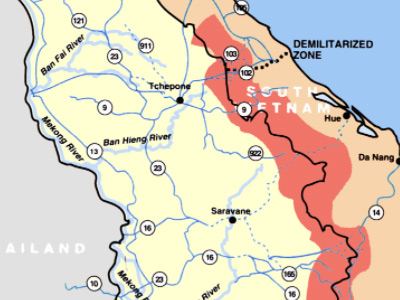
The Ho Chi Minh trail was used to supply the Viet Cong

In December 1960, the National Liberation Front (NLF, a.k.a. the Viet Cong) was formally created with the intent of uniting all anti-GVN activists, including non-communists. According to the Pentagon Papers, the Viet Cong "placed heavy emphasis on the withdrawal of American advisors and influence, on land reform and liberalization of the GVN, on coalition government and the neutralization of Vietnam." Often the leaders of the organization were kept secret.
Support for the NLF was driven by peasant resentment of Diem's reversal of land reforms in the countryside. The vast majority of the population lived in villages in the countryside, where a key demand was for land reform. In areas they controlled, the Viet Minh had confiscated large private landholdings, reduced rents and debts, and leased communal lands, mostly to the poorer peasants. Diem brought the landlords back to the villages. People who were farming land they had held for years now had to return it to landlords and pay years of back rent. This rent collection was enforced by the South Vietnamese army. The divisions within villages reproduced those that had existed against the French France, officially the French Republic is transcontinental country predominantly located in Western Europe and spanning overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. France reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under Napoleon Bonaparte, subjugating much of continental Europe and establishing the First French Empire.: "75 percent support for the NLF, 20 percent trying to remain neutral and 5 percent firmly pro-government."
France, officially the French Republic is transcontinental country predominantly located in Western Europe and spanning overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. France reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under Napoleon Bonaparte, subjugating much of continental Europe and establishing the First French Empire.: "75 percent support for the NLF, 20 percent trying to remain neutral and 5 percent firmly pro-government."
North Vietnamese Involvement
Sources disagree on whether North Vietnam played a direct role in aiding and organizing South Vietnamese rebels prior to 1960. Kahin and Lewis assert:
Contrary to United States policy assumptions, all available evidence shows that the revival of the civil war in the South in 1958 was undertaken by Southerners at their own—not Hanoi's—initiative…Insurgency activity against the Saigon government began in the South under Southern leadership not as a consequence of any dictate from Hanoi, but contrary to Hanoi's injunctions.
Similarly, historian Arthur Schlesinger Jr. states that "it was not until September, 1960 that the Communist Party of North Vietnam bestowed its formal blessing and called for the liberation of the south from American imperialism".
By contrast, James Olson and Randy Roberts assert that North Vietnam authorized a low-level insurgency in December 1956. To counter the accusation that North Vietnam was violating the Geneva Accord, the independence of the Viet Cong was stressed in communist propaganda.
In March 1956, southern communist leader Lê Duẩn presented a plan to revive the insurgency entitled "The Road to the South" to the other members of the Politburo in Hanoi, but as both China and the Soviets Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. The Soviet Union fall process began with growing unrest in the Union's various constituent national republics developing into an incessant political and legislative conflict between them and the central government. Estonia was the first Soviet republic to declare state sovereignty inside the Union. opposed confrontation at this time, Lê Duẩn's plan was rejected. However the North Vietnamese leadership approved tentative measures to revive the southern insurgency in December 1956. Communist forces were under a single command structure set up in 1958. The North Vietnamese Communist Party approved a "people's war" on the South at a session in January 1959 and in May, Group 559 was established to maintain and upgrade the Ho Chi Minh trail, at this time a six-month mountain trek through Laos. About 500 of the "regroupees" of 1954 were sent south on the trail during its first year of operation. The first arms delivery via the trail was completed in August 1959. About 40,000 communist soldiers infiltrated into the south from 1961–63.
Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. The Soviet Union fall process began with growing unrest in the Union's various constituent national republics developing into an incessant political and legislative conflict between them and the central government. Estonia was the first Soviet republic to declare state sovereignty inside the Union. opposed confrontation at this time, Lê Duẩn's plan was rejected. However the North Vietnamese leadership approved tentative measures to revive the southern insurgency in December 1956. Communist forces were under a single command structure set up in 1958. The North Vietnamese Communist Party approved a "people's war" on the South at a session in January 1959 and in May, Group 559 was established to maintain and upgrade the Ho Chi Minh trail, at this time a six-month mountain trek through Laos. About 500 of the "regroupees" of 1954 were sent south on the trail during its first year of operation. The first arms delivery via the trail was completed in August 1959. About 40,000 communist soldiers infiltrated into the south from 1961–63.
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Vietnam War (1955–1975)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.