War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802)

Peace Interrupted
From October 1797 until March 1799, the signatories of the Treaty of Campo Formio avoided armed conflict. Despite their agreement at Campo Formio, two primary combatants, France and Austria The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire., remained suspicious of each other and several diplomatic incidents undermined the agreement. The French demanded additional territory not mentioned in the Treaty. The Habsburgs were reluctant to hand over designated territories, much less additional ones. The Congress at Rastatt proved inept at orchestrating the transfer of territories to compensate the German princes for their losses. Ferdinand of Naples refused to pay tribute to France
The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire., remained suspicious of each other and several diplomatic incidents undermined the agreement. The French demanded additional territory not mentioned in the Treaty. The Habsburgs were reluctant to hand over designated territories, much less additional ones. The Congress at Rastatt proved inept at orchestrating the transfer of territories to compensate the German princes for their losses. Ferdinand of Naples refused to pay tribute to France In the history of France, French First Republic, sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic, was founded on 21 September 1792 during the French Revolution. The First Republic lasted until the declaration of the First Empire on 18 May 1804 under Napoléon Bonaparte, although the form of the government changed several times., followed by the Neapolitan rebellion and the subsequent establishment of the Parthenopaean Republic. Republicans in the Swiss cantons, supported by the French army, overthrew the central government in Bern and established the Helvetic Republic.
In the history of France, French First Republic, sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic, was founded on 21 September 1792 during the French Revolution. The First Republic lasted until the declaration of the First Empire on 18 May 1804 under Napoléon Bonaparte, although the form of the government changed several times., followed by the Neapolitan rebellion and the subsequent establishment of the Parthenopaean Republic. Republicans in the Swiss cantons, supported by the French army, overthrew the central government in Bern and established the Helvetic Republic.
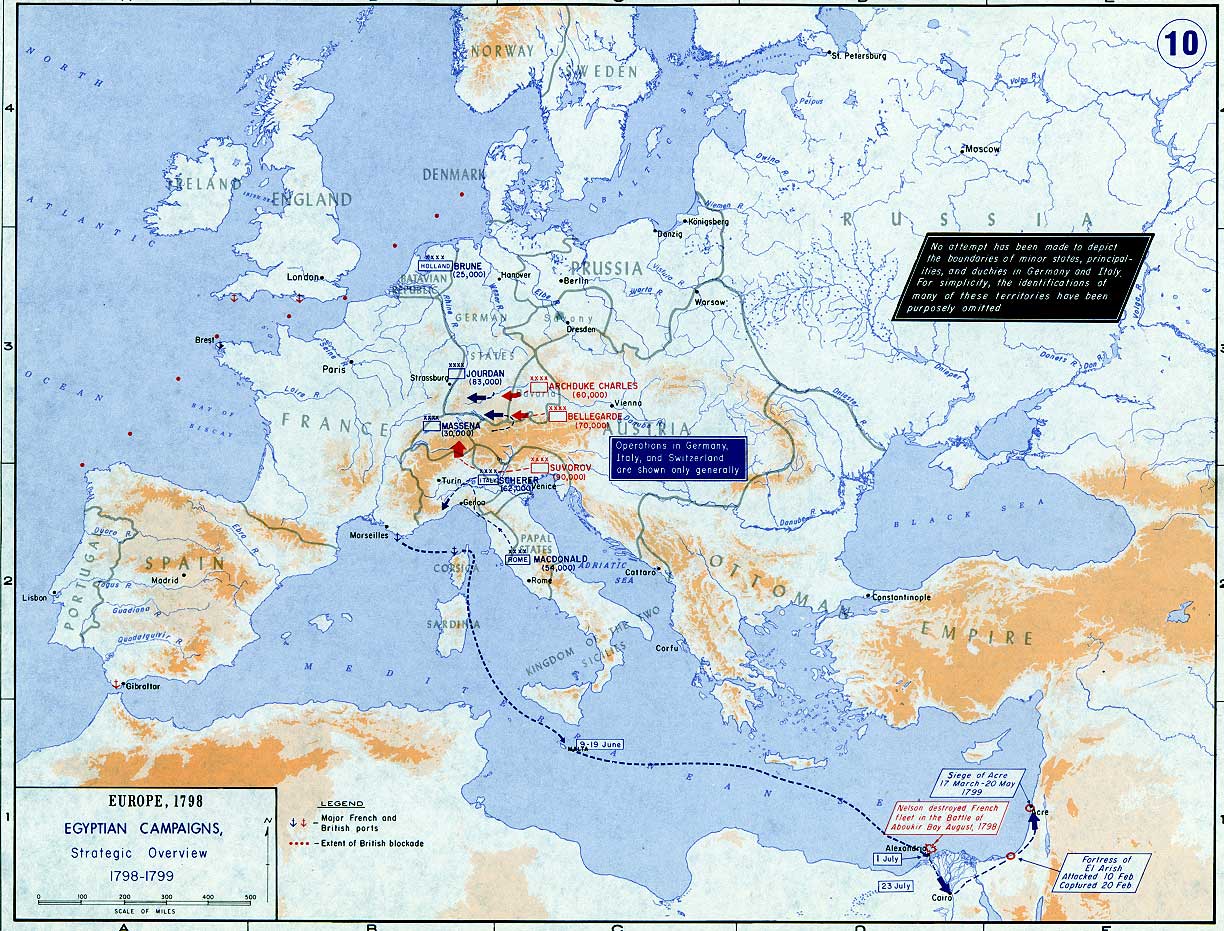
Strategic overview of operations in Europe and the Mediterranean in 1798–1799

Strategic overview of operations in Europe and the Mediterranean in 1798–1799
( Click image to enlarge)
Other factors contributed to the rising tensions. On his way to Egypt, Napoleon Napoleon Bonaparte (1769-1821), was a French military and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led several successful campaigns during the French Revolutionary Wars. As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814, and again in 1815. One of the greatest commanders in history, his wars and campaigns are studied at military schools worldwide. Napoleon Bonaparte » had stopped at the heavily fortified port city of Valletta. Grand Master Ferdinand von Hompesch zu Bolheim, who ruled the island, would only allow two ships at a time into the harbor, in accordance with the island's neutrality. Bonaparte immediately ordered the bombardment of Valletta and on 11 June, General Louis Baraguey d'Hilliers directed a landing of several thousand French troops at strategic locations around the island. The French Knights of the order deserted, and the remaining Knights failed to mount a successful resistance. Bonaparte forcibly removed the other Knights from their possessions, angering Paul, Tsar of Russia, who was the honorary head of the Order. The French Directory, furthermore, was convinced that the Austrians were conniving to start another war. Indeed, the weaker the French Republic seemed, the more seriously the Austrians, the Neapolitans, the Russians
Napoleon Bonaparte (1769-1821), was a French military and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led several successful campaigns during the French Revolutionary Wars. As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814, and again in 1815. One of the greatest commanders in history, his wars and campaigns are studied at military schools worldwide. Napoleon Bonaparte » had stopped at the heavily fortified port city of Valletta. Grand Master Ferdinand von Hompesch zu Bolheim, who ruled the island, would only allow two ships at a time into the harbor, in accordance with the island's neutrality. Bonaparte immediately ordered the bombardment of Valletta and on 11 June, General Louis Baraguey d'Hilliers directed a landing of several thousand French troops at strategic locations around the island. The French Knights of the order deserted, and the remaining Knights failed to mount a successful resistance. Bonaparte forcibly removed the other Knights from their possessions, angering Paul, Tsar of Russia, who was the honorary head of the Order. The French Directory, furthermore, was convinced that the Austrians were conniving to start another war. Indeed, the weaker the French Republic seemed, the more seriously the Austrians, the Neapolitans, the Russians Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. Russia remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire. and the British
Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. Russia remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire. and the British The Kingdom of Great Britain was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of England (which included Wales) and Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. actually discussed this possibility.
The Kingdom of Great Britain was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of England (which included Wales) and Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. actually discussed this possibility.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "War of the Second Coalition", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.










