Battle of Salamis (480 BC)

Battle
The actual battle of Salamis is not well described by the ancient sources, and it is unlikely that anyone (other than perhaps Xerxes) involved in the battle had a clear idea what was happening across the width of the straits. What follows is more of a discussion than a definitive account.
Dispositions
In the Allied fleet, the Athenians were on the left, and on the right were probably the Spartans (although Diodorus says it was the Megareans and Aeginetians); the other contingents were in the center. The Allied fleet probably formed into two ranks, since the straits would have been too narrow for a single line of ships. Herodotus has the Allied fleet in a line running north-south, probably with the northern flank off the coast of modern-day Saint George's Islet (Ayios Georgis), and the southern flank off the coast of Cape Vavari (part of Salamis). Diodorus suggests the Allied fleet was aligned east-west, spanning the straits between Salamis and Mount Aigaleo; however, it is unlikely that the Allies would have rested one of their flanks against Persian occupied territory.
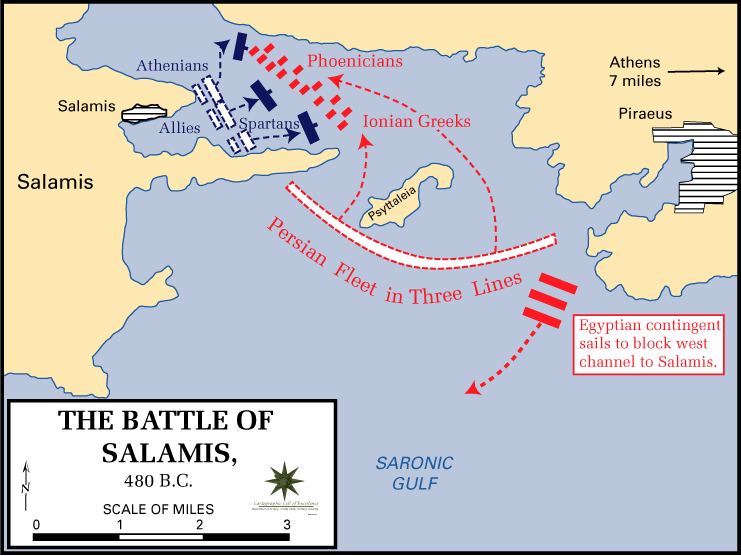
Battle of Salamis (480 BC)
It seems relatively certain that the Persian fleet was sent out to block the exit from the Straits the evening before the battle. Herodotus clearly believed that the Persian fleet actually entered the Straits at nightfall, planning to catch the Allies as they fled. However, modern historians have greatly debated this point, with some pointing out the difficulties of maneuvering in this confined space by night, and others accepting Herodotus's version. There are thus two possibilities; that during the night the Persians simply blocked the exit to the Straits, and then entered the straits in daylight; or that they entered the straits and positioned themselves for battle during the night. Regardless of when they attempted it, it seems likely that the Persians pivoted their fleet off the tip of Cape Vavari, so that from an initial east-west alignment (blocking the exit), they came round to a north-south alignment. The Persian fleet seems to have been formed into three ranks of ships (according to Aeschylus); with the powerful Phoenician fleet on the right flank next to Mount Aigaleo, the Ionian contingent on the left flank and the other contingents in the centre.
Diodorus says that the Egyptian fleet was sent to circumnavigate Salamis, and block the northern exit from the Straits. If Xerxes wanted to trap the Allies completely, this maneuver would have made sense (especially if he was not expecting the Allies to fight). However, Herodotus does not mention this (and possibly alludes to the Egyptian presence in the main battle), leading some modern historians to dismiss it; though again, others accept it as a possibility. Xerxes had also positioned around 400 troops on the island known as Psyttaleia, in the middle of the exit from the straits, in order to kill or capture any Greeks who ended up there (as a result of shipwreck or grounding).
The opening phase
Regardless of what time they entered the straits, the Persians did not move to attack the Allies until daylight. Since they were not planning to flee after all, the Allies would have been able to spend the night preparing for battle, and after a speech by Themistocles, the marines boarded and the ships made ready to sail. According to Herodotus, this was dawn, and as the Allies "were putting out to sea the barbarians immediately attacked them". If the Persians only entered the straits at dawn, then the Allies would have had the time to take up their station in a more orderly fashion.
Aeschylus claims that as the Persians approached (possibly implying that they were not already in the Straits at dawn), they heard the Greeks singing their battle hymn (paean) before they saw the Allied fleet:
ὦ παῖδες Ἑλλήνων ἴτε
ἐλευθεροῦτε πατρίδ᾽, ἐλευθεροῦτε δὲ
παῖδας, γυναῖκας, θεῶν τέ πατρῴων ἕδη,
θήκας τε προγόνων: νῦν ὑπὲρ πάντων ἀγών.
O sons of the Greeks, go,
Liberate your country, liberate
Your children, your women, the seats of your fathers' gods,
And the tombs of your forebears: now is the struggle for all things.
Herodotus recounts that, according to the Athenians, as the battle began the Corinthians hoisted their sails and began sailing away from the battle, northwards up the straits. However, he also says that other Greeks denied this story. If this did in fact occur, one possible interpretation is that these ships had been a decoy sent to reconnoitre the northern exit from the straits, in case the arrival of the encircling Egyptian detachment was imminent (if indeed this also occurred). Another possibility (not exclusive of the former) is that the departure of the Corinthians triggered the final approach of the Persians, suggesting as it did that the Allied fleet was disintegrating. At any rate, if they indeed ever left, the Corinthians soon returned to the battle.
Approaching the Allied fleet in the crowded Straits, the Persians appear to have become disorganised and cramped in the narrow waters. Moreover, it would have become apparent that, far from disintegrating, the Greek fleet was lined up, ready to attack them. However, rather than attacking immediately, the Allies initially appeared to back their ships away as if in fear. According to Plutarch, this was to gain better position, and also in order to gain time until the early morning wind. Herodotus recounts the legend that as the fleet had backed away, they had seen an apparition of a woman, asking them "Madmen, how far will ye yet back your ships?" However, he more plausibly suggests that whilst the Allies were backing water, a single ship shot forward to ram the nearest Persian vessel. The Athenians would claim that this was the ship of the Athenian Ameinias of Pallene; the Aeginetans would claim it as one of their ships. The whole Greek line then followed suit and made straight for the disordered Persian battle line.
The main battle
The details of the rest of the battle are generally sketchy, and no one involved would have had a view of the entire battlefield. Triremes were generally armed with a large ram at the front, with which it was possible to sink an enemy ship, or at least disable it by shearing off the banks of oars on one side. If the initial ramming was not successful, marines boarded the enemy ship and something similar to a land battle ensued. Both sides had marines on their ships for this eventuality; the Greeks with fully armed hoplites; the Persians probably with more lightly armed infantry.

Across the battlefield, as the first line of Persian ships was pushed back by the Greeks, they became fouled in the advancing second and third lines of their own ships. On the Greek left, the Persian admiral Ariabignes (a brother of Xerxes) was killed early in the battle; left disorganised and leaderless, the Phoenician squadrons appear to have been pushed back against the coast, many vessels running aground. In the centre, a wedge of Greek ships pushed through the Persians lines, splitting the fleet in two. According to Plutarch, Ariabignes was killed by Ameinias and Socles (Greek: Σωκλής) of Pallene. When Ariabignes attempted to board on their ship, they hit him with their spears, and thrust him into the sea. Plutarch also mentions that it was Artemisia who recognized Ariabignes' body floating among the shipwrecks and brought it back to Xerxes.
Herodotus recounts that Artemisia, the Queen of Halicarnassus, and commander of the Carian contingent, found herself pursued by the ship of Ameinias of Pallene. In her desire to escape, she attacked and rammed another Persian vessel, thereby convincing the Athenian captain that the ship was an ally; Ameinias accordingly abandoned the chase. However, Xerxes, looking on, thought that she had successfully attacked an Allied ship, and seeing the poor performance of his other captains commented that "My men have become women, and my women men". The friendly ship she sank was a Calyndian ship and the king of the Calyndians, Damasithymos (Greek: Δαμασίθυμος) was on it. None of the crew of the Calyndian ship survived.
The Persian fleet began to retreat towards Phalerum, but according to Herodotus, the Aeginetans ambushed them as they tried to leave the Straits. The remaining Persian ships limped back to the harbour of Phalerum and the shelter of the Persian army. The Athenian general Aristides then took a detachment of men across to Psyttaleia to slaughter the garrison that Xerxes had left there. The exact Persian casualties are not mentioned by Herodotus. However, he writes that the next year, the Persian fleet numbered 300 triremes. The number of losses then depends on the number of ships the Persian had to begin with; something in the range of 200–300 seems likely, based on the above estimates for the size of the Persian fleet. According to Herodotus, the Persians suffered many more casualties than the Greeks because most Persians did not know how to swim. Xerxes, sitting on Mount Aigaleo on his throne, witnessed the carnage. Some ship-wrecked Phoenician captains tried to blame the Ionians for cowardice before the end of the battle. Xerxes, in a foul mood, and having just witnessed an Ionian ship capture an Aeginetan ship, had the Phoenicians beheaded for slandering "more noble men". According to Diodorus, Xerxes "put to death those Phoenicians who were chiefly responsible for beginning the flight, and threatened to visit upon the rest the punishment they deserved", causing the Phoenicians to sail to Asia when night fell.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Battle of Salamis", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.









