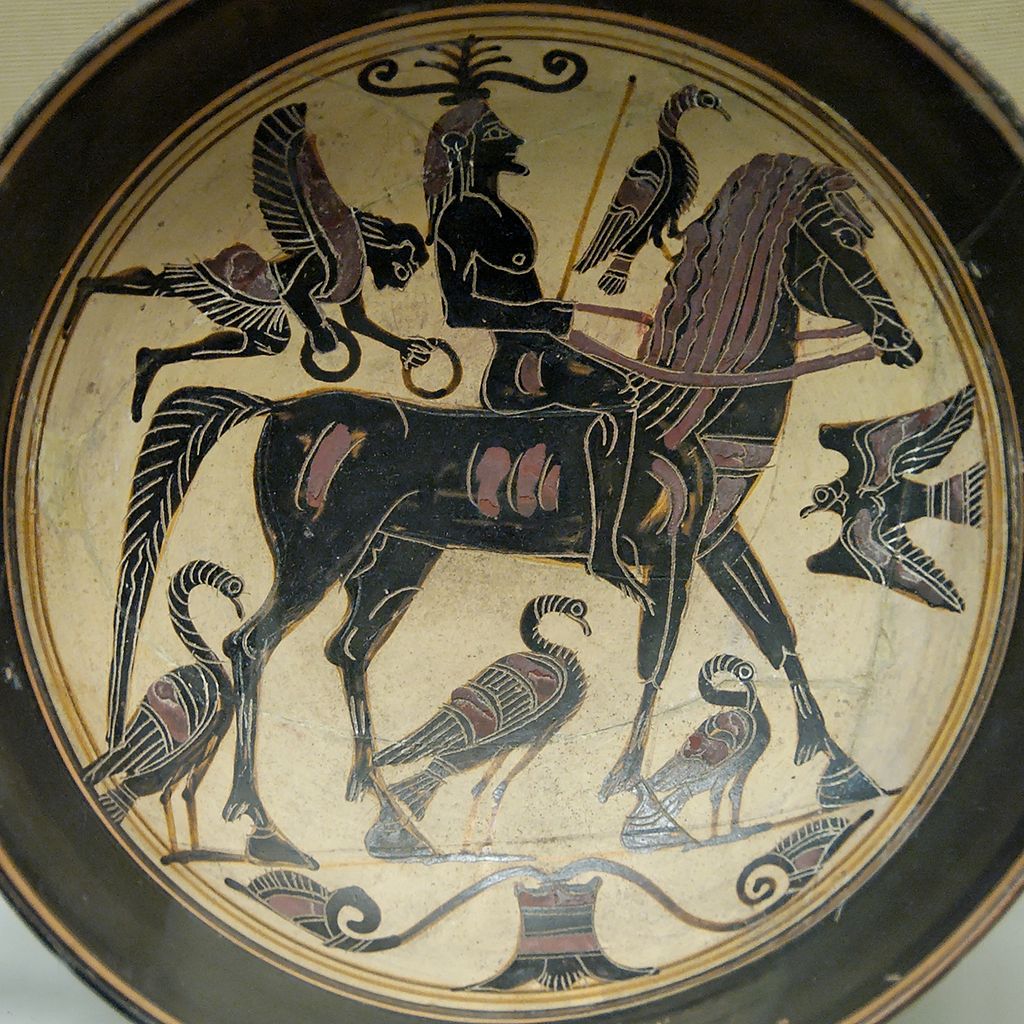
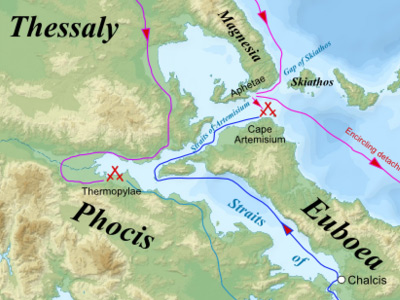
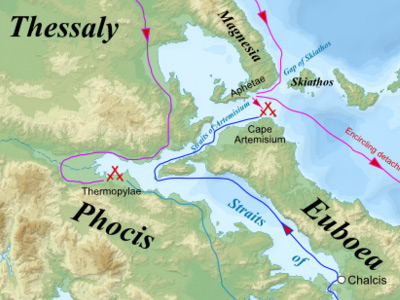
Battle of Thermopylae (480 BC)
Sources
The primary source for the Greco-Persian Wars is the Greek historian Herodotus. The Sicilian historian Diodorus Siculus, writing in the 1st century BC in his Bibliotheca historica, also provides an account of the Greco-Persian wars, partially derived from the earlier Greek historian Ephorus. This account is fairly consistent with Herodotus'. The Greco-Persian wars are also described in less detail by a number of other ancient historians including Plutarch, Ctesias of Cnidus, and are referred to by other authors, as in Aeschylus in The Persians.
Archaeological evidence, such as the Serpent Column (now in the Hippodrome of Constantinople), also supports some of Herodotus' specific claims. George B. Grundy was the first modern historian to do a thorough topographical survey of the narrow pass at Thermopylae, and to the extent that modern accounts of the battle differ from Herodotus' they usually follow Grundy's. For example, the military strategist Sir Basil Henry Liddell Hart defers to Grundy. Grundy also explored Plataea and wrote a treatise on that battle.
On the Battle of Thermopylae itself, two principal sources, Herodotus' and Simonides' accounts, survive. In fact, Herodotus' account of the battle, in Book VII of his Histories, is such an important source that Paul Cartledge wrote: "we either write a history of Thermopylae with [Herodotus], or not at all". Also surviving is an epitome of the account of Ctesias', by the eighth-century Byzantine Photias, though this is "almost worse than useless", missing key events in the battle such as the betrayal of Ephialtes, and the account of Diodorus Siculus' in his Universal History. Diodorus' account seems to have been based on that of Ephorus and contains one significant deviation from Herodotus' account: a supposed night attack against the Persian camp, of which modern scholars have tended to be skeptical.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Battle of Thermopylae", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.