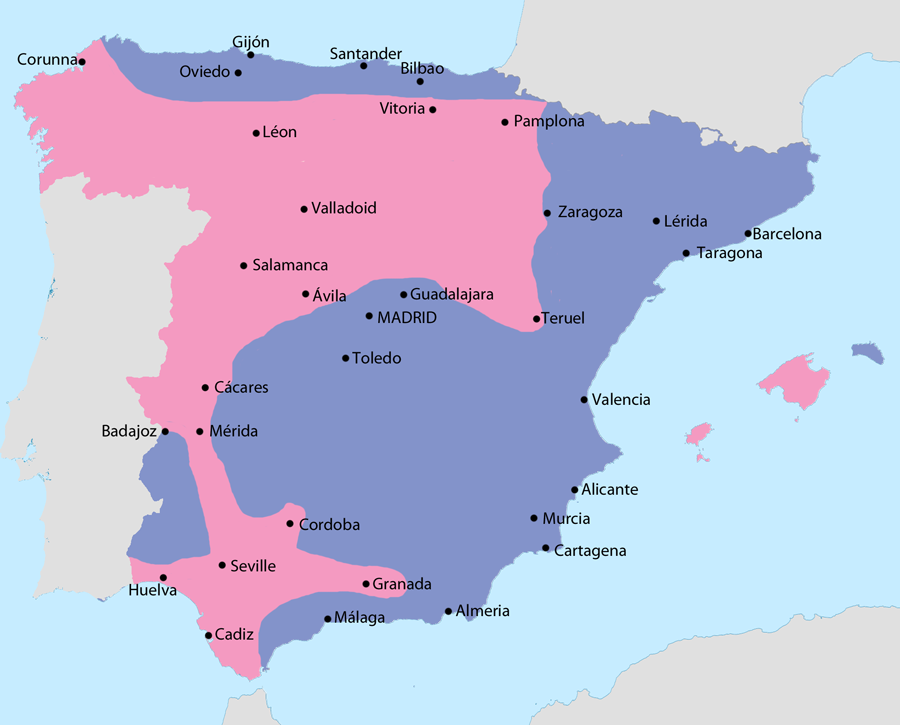
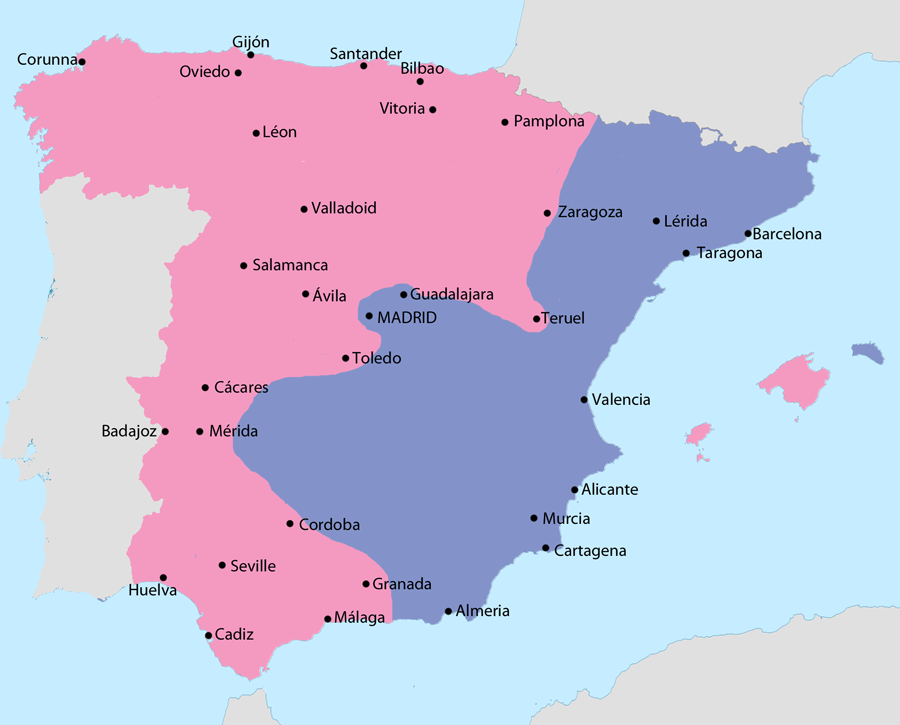
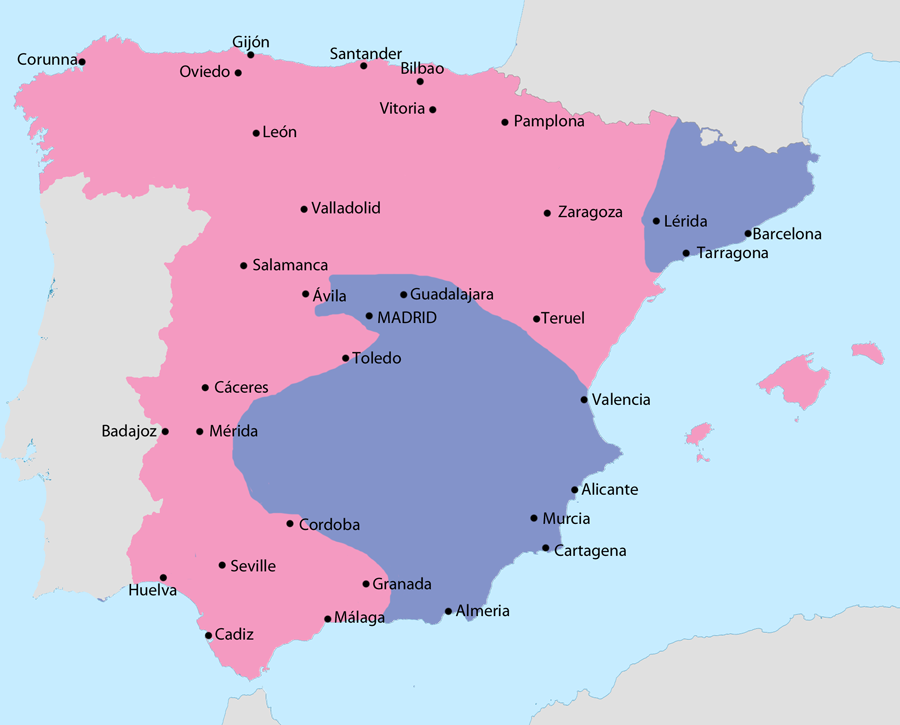
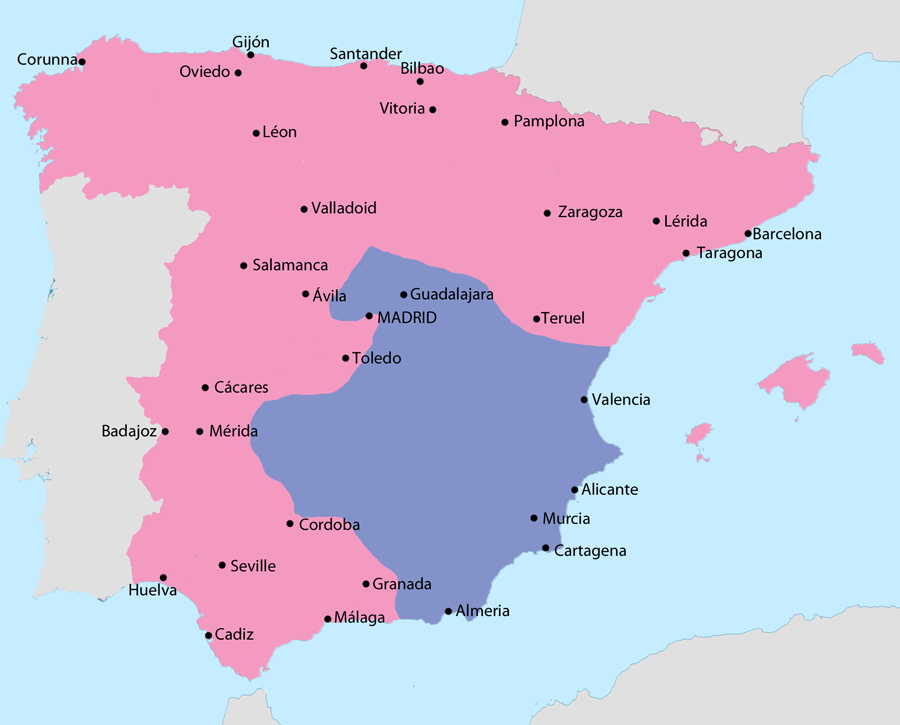
Spanish Civil War (1936 to 1939)

Background
The 19th century was a turbulent time for Spain. Those in favour of reforming Spain's government vied for political power with conservatives, who tried to prevent reforms from taking place. Some liberals, in a tradition that had started with the Spanish Constitution of 1812, sought to limit the power of the monarchy of Spain and to establish a liberal state. The reforms of 1812 did not last after King Ferdinand VII dissolved the Constitution and ended the Trienio Liberal government. Twelve successful coups were carried out between 1814 and 1874. Until the 1850s, the economy of Spain was primarily based on agriculture. There was little development of a bourgeois industrial or commercial class. The land-based oligarchy remained powerful; a small number of people held large estates called latifundia as well as all the important government positions.
In 1868 popular uprisings led to the overthrow of Queen Isabella II of the House of Bourbon. Two distinct factors led to the uprisings: a series of urban riots and a liberal movement within the middle classes and the military (led by General Joan Prim) concerned with the ultra-conservatism of the monarchy. In 1873 Isabella's replacement, King Amadeo I of the House of Savoy, abdicated owing to increasing political pressure, and the short-lived First Spanish Republic was proclaimed. After the restoration of the Bourbons in December 1874, Carlists and Anarchists emerged in opposition to the monarchy. Alejandro Lerroux, Spanish politician and leader of the Radical Republican Party, helped bring republicanism to the fore in Catalonia, where poverty was particularly acute. Growing resentment of conscription and of the military culminated in the Tragic Week in Barcelona in 1909.
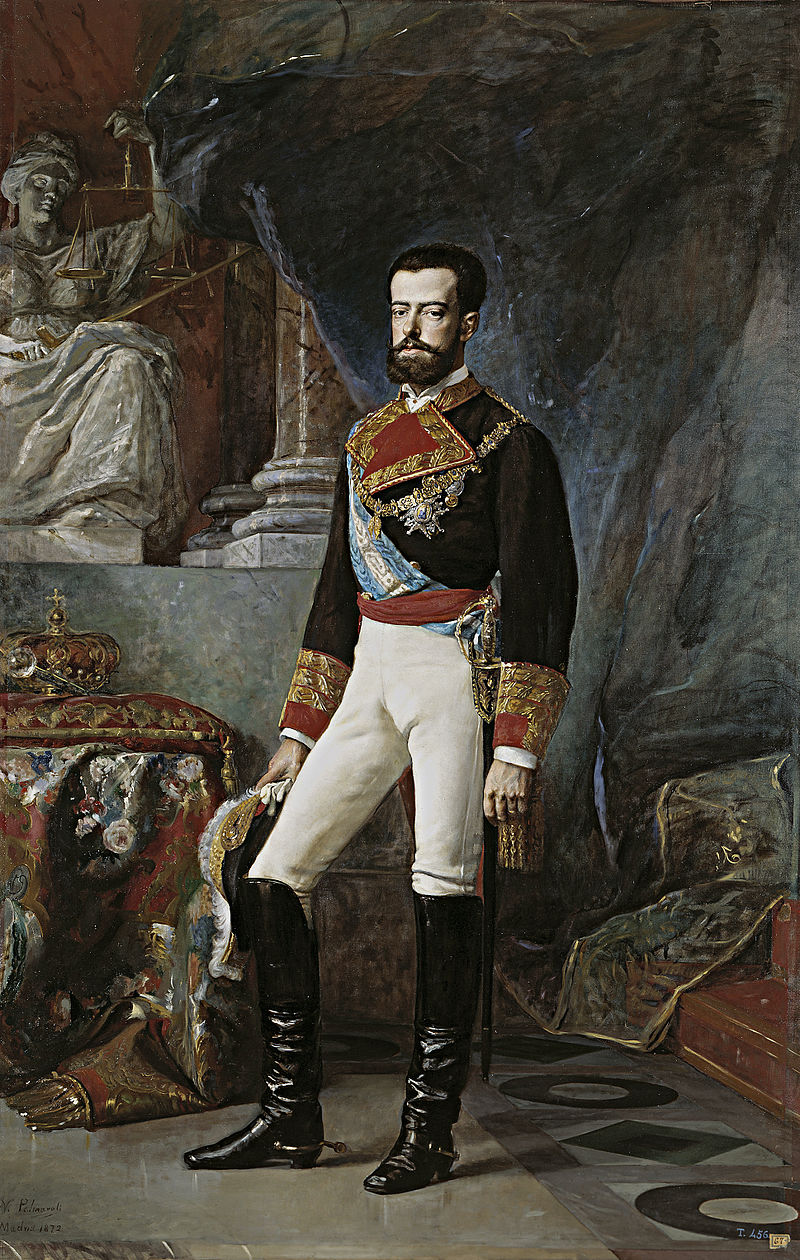

Amadeo (Italian Amedeo, sometimes anglicized as Amadeus) ( 30 May 1845 – 18 January 1890) was the only King of Spain from the House of Savoy. He was the second son of King Victor Emmanuel II of Italy and was known for most of his life as Duke of Aosta, but served briefly as King of Spain from 1870 to 1873. Granted the hereditary title Duke of Aosta in the year.
Spain was neutral in World War I World War I, also known as the First World War, or the Great War, was a global war originating in Europe that lasted from 28 July 1914 to 11 November 1918. More than 70 million military personnel, including 60 million Europeans, were mobilized in one of the largest wars in history. The war drew in all the world's economic great powers, assembled in two opposing alliances: the Allies versus the Central Powers of Germany and Austria-Hungary. View World War I ». Following the war, the working class, industrial class, and military united in hopes of removing the corrupt central government, but were unsuccessful. Popular perception of communism as a major threat significantly increased during this period. In 1923 a military coup brought Miguel Primo de Rivera to power; as a result, Spain transitioned to government by military dictatorship. Support for the Rivera regime gradually faded, and he resigned in January 1930. He was replaced by General Dámaso Berenguer, who was in turn himself replaced by Admiral Juan Bautista Aznar-Cabañas; both men continued a policy of rule by decree. There was little support for the monarchy in the major cities. Consequently, King Alfonso XIII gave in to popular pressure for the establishment of a republic in 1931 and called municipal elections for 12 April of that year. The socialist and liberal republicans won almost all the provincial capitals, and following the resignation of Aznar's government, King Alfonso XIII fled the country. At this time, the Second Spanish Republic was formed and would remain in power until the culmination of the Spanish Civil War.
World War I, also known as the First World War, or the Great War, was a global war originating in Europe that lasted from 28 July 1914 to 11 November 1918. More than 70 million military personnel, including 60 million Europeans, were mobilized in one of the largest wars in history. The war drew in all the world's economic great powers, assembled in two opposing alliances: the Allies versus the Central Powers of Germany and Austria-Hungary. View World War I ». Following the war, the working class, industrial class, and military united in hopes of removing the corrupt central government, but were unsuccessful. Popular perception of communism as a major threat significantly increased during this period. In 1923 a military coup brought Miguel Primo de Rivera to power; as a result, Spain transitioned to government by military dictatorship. Support for the Rivera regime gradually faded, and he resigned in January 1930. He was replaced by General Dámaso Berenguer, who was in turn himself replaced by Admiral Juan Bautista Aznar-Cabañas; both men continued a policy of rule by decree. There was little support for the monarchy in the major cities. Consequently, King Alfonso XIII gave in to popular pressure for the establishment of a republic in 1931 and called municipal elections for 12 April of that year. The socialist and liberal republicans won almost all the provincial capitals, and following the resignation of Aznar's government, King Alfonso XIII fled the country. At this time, the Second Spanish Republic was formed and would remain in power until the culmination of the Spanish Civil War.
The revolutionary committee headed by Niceto Alcalá-Zamora became the provisional government, with Alcalá-Zamora as president and head of state. The republic had broad support from all segments of society. In May, an incident where a taxi driver was attacked outside a monarchist club sparked anti-clerical violence throughout Madrid and south-west Spain. The government's slow response disillusioned the right and reinforced their view that the Republic was determined to persecute the church. In June and July the Confederación Nacional del Trabajo (CNT) called several strikes, which led to a violent incident between CNT members and the Civil Guard and a brutal crackdown by the Civil Guard and the army against the CNT in Seville. This led many workers to believe the Spanish Second Republic was just as oppressive as the monarchy and the CNT announced their intention of overthrowing it via revolution. Elections in June 1931 returned a large majority of Republicans and Socialists. With the onset of the Great Depression, the government attempted to assist rural Spain by instituting an eight-hour day and giving land tenure to farm workers.
Fascism remained a reactive threat, helped by controversial reforms to the military. In December a new reformist, liberal, and democratic constitution was declared. It included strong provisions enforcing a broad secularization of the Catholic country, which many moderate committed Catholics opposed. Republican Manuel Azaña became prime minister of a minority government in October 1931. In 1933 the parties of the right won the general elections, largely owing to the anarchists' abstention from the vote, increased right-wing resentment of the incumbent government caused by a controversial decree implementing land reform, the Casas Viejas incident, and the formation of a right-wing alliance, Spanish Confederation of Autonomous Right-wing Groups (CEDA). The recent enfranchisement of women, most of whom voted for centre-right parties, was also a contributing factor.
Events in the period following November 1933, called the "black two years", seemed to make a civil war more likely. Alejandro Lerroux of the Radical Republican Party (RRP) formed a government, reversing changes made under the previous administration and granting amnesty to the collaborators of the unsuccessful uprising by General José Sanjurjo in August 1932. Some monarchists joined with the then fascist-nationalist Falange Española y de las JONS ("Falange") to help achieve their aims. Open violence occurred in the streets of Spanish cities, and militancy continued to increase, reflecting a movement towards radical upheaval, rather than peaceful democratic means as solutions.
In the last months of 1934, two government collapses brought members of the CEDA into the government. Farm workers' wages were cut in half, and the military was purged of Republican members. A popular front alliance was organized, which narrowly won the 1936 elections. Azaña led a weak minority government, but soon replaced Zamora as president in April. Prime Minister Santiago Casares Quiroga ignored warnings of a military conspiracy involving several generals, who decided that the government had to be replaced to prevent the dissolution of Spain.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Spanish Civil War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.